A new report, seeking to study how the Indian state has allegedly weaponised the Unlawful Activities Prevention Act (UAPA) "against anyone who dares to challenge the Indian state and assert their fundamental rights to information, association, dissent and democracy", has said that the NDA government led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi is indiscriminately using the National Investigation Agency (NIA) as the "lead player in the abuse of UAPA."
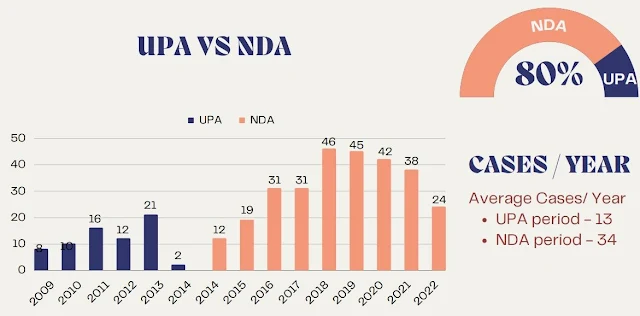
Published by the People’s Union for Civil Liberties (PUCL) and authored by V Suresh, Madhura SB and Lekshmi Sujatha, the report, titled "UAPA: Criminalising Dissent and State Terror: Study of UAPA Abuse in India, 2009 - 2022", released as part of its #RepealUAPA Campaign says that out of a total of 357 UAPA cases handled by NIA between the period 2009-August 2022, about 20% were registered and investigated during the Manmohan Singh led regime, while 80% were registered and investigated during the Modi government.The report says, a study of the NIA website data shows that of the 357 UAPA cases investigated by the NIA, 41 or 12% were registered suo motu, while a whopping 316 or 88% were transferred to NIA from state police.
Noting that NIA having suo motu powers to transfer investigations from state police is a "threat to federalism", the report says, the most contentious use of such wide powers was in the manner the Ministry of Home Affairs overnight decided to transfer the Bhima Koregaon case in early 2020 from the Maharashtra state police to NIA only because the Fadnavis-led BJP government fell and a new MVA government led by Uddhav Thackeray took charge.
According to the report, the validity of these transfers from the state police to the NIA is also suspect since a high number of these transferred cases were not even remotely connected to national security or threat to sovereignty or involved any violence.
It adds, an example is a case from Madurai involving a Facebook post on August 15, 2019 in which the accused person remarked as to whether India was truly independent. The case was abruptly transferred from the Tamil Nadu state police to NIA in 2021.
Referring to what it calls "abuse of the conspiracy provision", the report says, an analysis of use of Section 18 of UAPA titled Punishment for Conspiracy suggests, an alleged agreement to commit a terrorist crime is enough to prosecute; the “object” of the agreement need not have occurred. "The definition of conspiracy is so wide and elastic, that anyone can be roped in", it stresses.
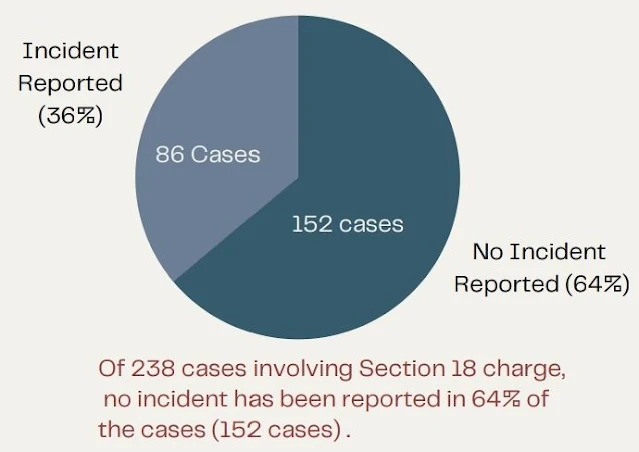
An examination of the number of cases under Section 18 UAPA offences reveals that out of total UAPA cases investigated by NIA (357), the cases involving Section 18 charges were 238. Of these 238 cases, the cases where some incident of terrorism occurred were 86 cases (36%), while cases where no specific incident involving weapons or causing physical injury were 152 cases (64%).
In other words, the report says, in 64% of cases involving the Section 18 UAPA charge, the mere allegation of the police that a person is a member of a proscribed terrorist organisation or some recoveries were made from him of an alleged weapon or explosives or drugs or money is sufficient to arrest the person and be imprisoned for many years.
The report, which is based on an analysis of the National Crimes Records Bureau (NCRB) statistics -- calling it the only data source, albeit sketchy and available for the period 2015 till 2020 -- shedding light poor conviction rate vis-à-vis the impossibility of bail in UAPA cases, says, there were 5,924 UAPA cases registered throughout India in which 8,371 persons were arrested during 2015-2020.
Thus, according to the report, in the years 2018 and 2020, the percentage of people on bail was as low as 16.32% and 16.88%, and the figure for 2019 reflected a higher proportion of 32.08%. However, it underlines, a closer study reveals that in Tamil Nadu in 2019, all 308 persons shown as arrested under UAPA were released on bail, which is highly unusual for UAPA cases. If these cases are kept aside, the bail percentage is seen to be 16.27%.
As for the conviction rates, if based on the number of cases, they are 27.57%, but the conviction rates based on number of persons arrested is a mere 2.80%, the report says. It comments, the poor conviction rate of 2.8% based on number of persons arrested in UAPA cases is in line with the conviction rates when the previous anti-terror legislations TADA (P) Act and POTA were in vogue.
The report continues, if looked at in another way, out of 8,371 persons arrested during 2015-2020 under UAPA, close to 8,136 persons constituting 97.2% of persons arrested, got acquitted at the end of trials in UAPA courts but after spending many years in jail without bail. Such high acquittal rates, only highlights the fact that most of the prosecutions are devoid of merit and did not warrant initiation of prosecution in the first place, much less, under UAPA.
The report, seeking wider media to educate people about the dangers of such laws, demands repeal of UAPA and repeal of all other anti-people laws; repeal of the NIA Act and disbanding of NIA; immediate release of all political prisoners, on bail; action against all police officials who have wilfully launched false and fabricated cases against marginalised communities, journalists, academicians, students and others; and reparations for those wrongfully accused and released by courts.
Thus, according to the report, in the years 2018 and 2020, the percentage of people on bail was as low as 16.32% and 16.88%, and the figure for 2019 reflected a higher proportion of 32.08%. However, it underlines, a closer study reveals that in Tamil Nadu in 2019, all 308 persons shown as arrested under UAPA were released on bail, which is highly unusual for UAPA cases. If these cases are kept aside, the bail percentage is seen to be 16.27%.
As for the conviction rates, if based on the number of cases, they are 27.57%, but the conviction rates based on number of persons arrested is a mere 2.80%, the report says. It comments, the poor conviction rate of 2.8% based on number of persons arrested in UAPA cases is in line with the conviction rates when the previous anti-terror legislations TADA (P) Act and POTA were in vogue.
The report continues, if looked at in another way, out of 8,371 persons arrested during 2015-2020 under UAPA, close to 8,136 persons constituting 97.2% of persons arrested, got acquitted at the end of trials in UAPA courts but after spending many years in jail without bail. Such high acquittal rates, only highlights the fact that most of the prosecutions are devoid of merit and did not warrant initiation of prosecution in the first place, much less, under UAPA.
The report, seeking wider media to educate people about the dangers of such laws, demands repeal of UAPA and repeal of all other anti-people laws; repeal of the NIA Act and disbanding of NIA; immediate release of all political prisoners, on bail; action against all police officials who have wilfully launched false and fabricated cases against marginalised communities, journalists, academicians, students and others; and reparations for those wrongfully accused and released by courts.



Comments