Counterview Desk
Pointing out that India’s hydro generation remains around 10% for the last six years, the advocacy group South Asia Network on Dams, Rivers and People (SANDRP) has said that power generation from hydropower projects continues to show diminishing returns, as has been the story close to three decades now.
Yet, says SANDRP in a note, the Government of India continues to push large hydro by announcing a slew of additional subsidies for hydropower projects, more for political economy reason. In fact, attempts are being made to flog unviable hydropower projects with various kind of manipulations, illegalities and violations, it adds.
Projects with installed capacity above 25 MW as projects with installed capacity below 25MW are called small hydro.
The South West Monsoon Rainfall was 10.46 % above normal in 2018-19, 8.74% above normal in 2019-20, 0.7% above normal in 2020-21 and 6.8% above normal in 2021-22. The October rainfall has also been generally above normal in recent years. These have helped the hydropower generation go marginally up above 10% in last three years.
In 2016-17, for the first time in independent India’s history, power generation from large hydropower projects in India fell below 10% of total electricity generation and remained below 10% for the next three years: 2016-17, 2017-18 and 2018-19. This analysis is based on actual generation (measured as million or billion Units) as reported by Central Electricity Authority (CEA) and not installed capacity (measured in Mega Watts).
One unit equals one Kilowatt hour, which is the power generated when 1 KW of installed capacity runs for one hour. The units are actually consumable and provide the correct picture of power available for consumption.
For the latest year ending on March 31, 2022, the power generation from large hydropower projects (CEA only reports large hydro generation) in 2021-22 was 151.63 BU, when total power generation in India (including renewables generation of 181.37 BU, but excluding Bhutan imports of 7.49 BU) was 1491.86 BU, hence hydropower generation in 2021-22 was 10.86% of total electricity generation.
The hydropower generation proportion to total electricity generation was 9.90% in 2016-17; 9.68% in 2017-18 and 9.84% in 2018-19, 11.26% in 2019-20 and 11.62% in 2020-22. Reduced overall generation due to Covid Pandemic was also a reason for increased proportion of hydropower generation to total generation in 2019-20, 2020-21 and 2021-22.
Diminishing returns, Declining proportion However, power generation from hydropower projects continues to show diminishing returns, as has been the story close to three decades now, see the trend-line in graph below where we have plotted MU electricity generated per MW hydro installed capacity over the years since 1993-94.
Similarly, the proportion of hydropower in overall electricity generation continues to show declining proportion, slight increase in last three years notwithstanding. Some of the major reasons for this declining proportion of hydropower generation are: diminishing generation of existing hydropower projects in India (see the graph above) and large hydropower projects becoming more and more unviable.
Even NHPC chief agrees they are unviable. As the then power minister of India stated in the Parliament, at least 15 large hydro projects (NHPC chief says 40 HEPs need bailout package, see below) with capacity close to 6000 MW remains stranded in India.
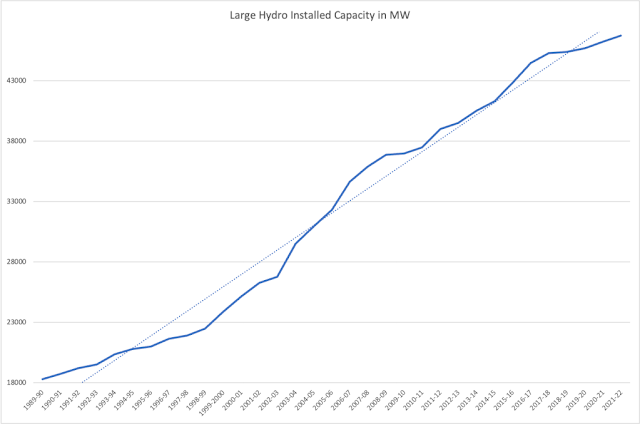
A direct fall out of this could be seen in the capacity addition trends, see the chart below, where we can see the flattening of the graph in latest years. The capacity addition that was 7028 MW in 1999-2004 and 5371 MW in 2004-09 has fallen to 3646 during 2009-2014 and 4875 MW during 2014-19. In the latest five years (2017-22) capacity addition has been 2242 MW.
Union Power Minister RK Singh said, the power ministry is pushing state-run majors under its wings to take over 29 hydel projects with combined capacity of 30 000 MW entailing estimated investments of up to Rs 2.7 lakh crore (much more in reality) that are languishing with private developers.
None of these are going to help the cause of large hydro projects. The government needs to understand that even these additional subsidies for the already over subsidized hydropower sector is not going to help make them viable. When solar and wind power is available at price below Rs 3 per unit, why is there attempt to push large hydro whose cost is universally over Rs 5-6 per unit or more. Why should the government spend public money through PSUs to push such unviable projects?
It may be noted here that in recent years, the big hydro projects are facing increasing accidents and disasters and this is only likely to increasing with changing climate.
In conclusion India needs to pay attention to optimizing generation from existing hydro and explore the possibilities of installing hydro projects at 97% of India’s existing large dams where there is no hydro component.
We also need to first manage our peak hours’ power demand and optimize generation from existing hydro during peak hours, only after assessing and addressing the social and environmental impacts of peaking hour power generation from large hydro projects.
Else we will be destroying more rivers and their biodiversity and livelihoods of people dependent on such rivers, while throwing more money into the pockets of consultants, contractors, equipment suppliers, cement companies and other vested interests.
The Ministry of Environment and Forests and its Expert Appraisal Committee on River Valley Projects too needs take this opportunity to improve their pathetic environmental governance rather than keep pushing more clearances for projects through corruption, manipulations and violations.
Pointing out that India’s hydro generation remains around 10% for the last six years, the advocacy group South Asia Network on Dams, Rivers and People (SANDRP) has said that power generation from hydropower projects continues to show diminishing returns, as has been the story close to three decades now.
Yet, says SANDRP in a note, the Government of India continues to push large hydro by announcing a slew of additional subsidies for hydropower projects, more for political economy reason. In fact, attempts are being made to flog unviable hydropower projects with various kind of manipulations, illegalities and violations, it adds.
Text:
In last six years, from 2016-17 to 2021-22, India’s large hydropower projects (projects above 25 MW installed capacity) have contributed just around 10% of the total power generation, going as low as 9.68% in 2017-18. In fact, in three of these six years, large hydro contributed less than 10% and recovering only marginally in the rest, thanks to surplus monsoon.Projects with installed capacity above 25 MW as projects with installed capacity below 25MW are called small hydro.
The South West Monsoon Rainfall was 10.46 % above normal in 2018-19, 8.74% above normal in 2019-20, 0.7% above normal in 2020-21 and 6.8% above normal in 2021-22. The October rainfall has also been generally above normal in recent years. These have helped the hydropower generation go marginally up above 10% in last three years.
In 2016-17, for the first time in independent India’s history, power generation from large hydropower projects in India fell below 10% of total electricity generation and remained below 10% for the next three years: 2016-17, 2017-18 and 2018-19. This analysis is based on actual generation (measured as million or billion Units) as reported by Central Electricity Authority (CEA) and not installed capacity (measured in Mega Watts).
One unit equals one Kilowatt hour, which is the power generated when 1 KW of installed capacity runs for one hour. The units are actually consumable and provide the correct picture of power available for consumption.
For the latest year ending on March 31, 2022, the power generation from large hydropower projects (CEA only reports large hydro generation) in 2021-22 was 151.63 BU, when total power generation in India (including renewables generation of 181.37 BU, but excluding Bhutan imports of 7.49 BU) was 1491.86 BU, hence hydropower generation in 2021-22 was 10.86% of total electricity generation.
The hydropower generation proportion to total electricity generation was 9.90% in 2016-17; 9.68% in 2017-18 and 9.84% in 2018-19, 11.26% in 2019-20 and 11.62% in 2020-22. Reduced overall generation due to Covid Pandemic was also a reason for increased proportion of hydropower generation to total generation in 2019-20, 2020-21 and 2021-22.
Diminishing returns, Declining proportion However, power generation from hydropower projects continues to show diminishing returns, as has been the story close to three decades now, see the trend-line in graph below where we have plotted MU electricity generated per MW hydro installed capacity over the years since 1993-94.
Similarly, the proportion of hydropower in overall electricity generation continues to show declining proportion, slight increase in last three years notwithstanding. Some of the major reasons for this declining proportion of hydropower generation are: diminishing generation of existing hydropower projects in India (see the graph above) and large hydropower projects becoming more and more unviable.
Even NHPC chief agrees they are unviable. As the then power minister of India stated in the Parliament, at least 15 large hydro projects (NHPC chief says 40 HEPs need bailout package, see below) with capacity close to 6000 MW remains stranded in India.
A direct fall out of this could be seen in the capacity addition trends, see the chart below, where we can see the flattening of the graph in latest years. The capacity addition that was 7028 MW in 1999-2004 and 5371 MW in 2004-09 has fallen to 3646 during 2009-2014 and 4875 MW during 2014-19. In the latest five years (2017-22) capacity addition has been 2242 MW.
The government continues to push large hydro
On March 8, 2019, on the eve of India’s last general elections, the Union Government declared a slew of additional subsidies for hydropower projects, but this seemed more for political economy reason, as also suggested by the timing of the announcement, just before the model code of conduct came into force on March 11, 2019. There are many other attempts being made to flog the unviable hydropower projects with various kind of manipulations, illegalities and violations. Just a couple of instances are narrated below:- State-owned hydro power giant NHPC signed a pact with Cement Corporation of India (CCI) for meeting cement requirements of the Dibang Project. This happened in 2020 when CCI coming under the Ministry of Heavy Industries and Prakash Javdekar happened to be both the minister of heavy industries and Environment and Forests. And it is MoEF that issues the forest clearance! Earlier on July 17, 2020, the Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs, chaired by the Prime Minister, approved Rs 1,600 crore for “pre-investment activities and various clearances” of the project.
- Jindal Power Ltd Chief Executive Officer Bharat Rohra said, generation glut in hydropower project had made an estimated $3.3 billion facility a risky bet for the company to handle: “In the current situation, the project doesn’t look like an attractive investment in view of the huge investment. Further, it is a large project and we feel we’ll struggle to find long-term buyers for the entire capacity but policy support from the government can make the project viable and draw investors.”
Union Power Minister RK Singh said, the power ministry is pushing state-run majors under its wings to take over 29 hydel projects with combined capacity of 30 000 MW entailing estimated investments of up to Rs 2.7 lakh crore (much more in reality) that are languishing with private developers.
None of these are going to help the cause of large hydro projects. The government needs to understand that even these additional subsidies for the already over subsidized hydropower sector is not going to help make them viable. When solar and wind power is available at price below Rs 3 per unit, why is there attempt to push large hydro whose cost is universally over Rs 5-6 per unit or more. Why should the government spend public money through PSUs to push such unviable projects?
It may be noted here that in recent years, the big hydro projects are facing increasing accidents and disasters and this is only likely to increasing with changing climate.
In conclusion India needs to pay attention to optimizing generation from existing hydro and explore the possibilities of installing hydro projects at 97% of India’s existing large dams where there is no hydro component.
We also need to first manage our peak hours’ power demand and optimize generation from existing hydro during peak hours, only after assessing and addressing the social and environmental impacts of peaking hour power generation from large hydro projects.
Else we will be destroying more rivers and their biodiversity and livelihoods of people dependent on such rivers, while throwing more money into the pockets of consultants, contractors, equipment suppliers, cement companies and other vested interests.
The Ministry of Environment and Forests and its Expert Appraisal Committee on River Valley Projects too needs take this opportunity to improve their pathetic environmental governance rather than keep pushing more clearances for projects through corruption, manipulations and violations.

.jpeg)

Comments