
By A Representative
Data of Socio-Economic and Caste Census (SECC) 2011 for Rural India, released recently by Finance Minister Arun Jaitley, gives a unique opportunity to scholars and policy makers to make inter-state comparisons, suggesting how different rural areas of the country are performing across India. Based on household data taken from the National Population Register along with the Temporary Identification Number (TIN), the survey, say policy makers, can be used in evidence based planning for rural development and poverty reduction. Dealing with different aspects of their socio-economic status, some of the more prominent indicators suggest, given in the form of charts below, the level of prosperity and deprivation in selected fields in different states.
They also suggest where does rural Gujarat, touted as a “model” by the powers that be for other states to follow, stands vis-à-vis other states. Collected in 2012-13, despite claimed double digit agricultural growth, which many experts have doubted, as one can see, Gujarat is, at best, an average performer in income and asset ownership. Some of the highlights of inter-state comparison:
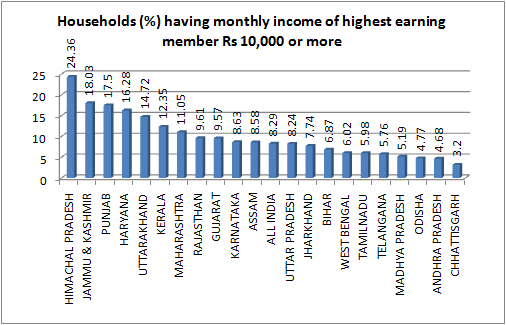
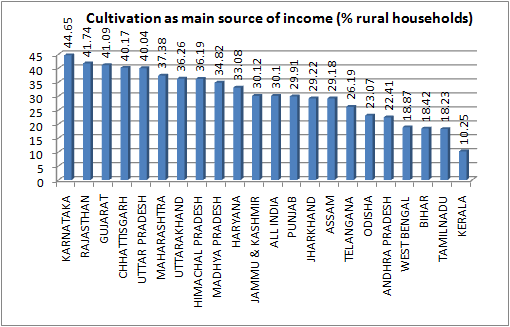
1. The data on income suggest that while in India as a whole nearly 92 per cent of the highest earning members of the rural households earn less than Rs 10,000 per month, in Gujarat there are about 89 per cent such households, about the same.2. In the country as a whole, there are 30.1 per cent rural households who are mainly dependent on cultivation to earn a livelihood. By comparison, in Gujarat, 40.1 per cent rural households depend on cultivation.
3. In Gujarat, there are 43.28 per cent rural households which depend mainly on manual casual labour to earn livelihood, as against the all-India average of 51.14 per cent.4. There are 55 per cent of the rural households which have no land to cultivate, as against the all-India average of about the same, 56 per cent.5. In Gujarat, there are 52 per cent rural households whose agriculture has to depend on the vagaries of nature. They own unirrigated land. The all-India average is far less — 40 per cent.6. Gujarat’s 33 per cent of households enjoy the advantage of irrigating their fields and sowing two crops, as against the all-India average of 37 per cent.7. Gujarat’s 44.69 per cent of households live in kuccha houses, which is one of the highest in the country. Even national average is is a little less — 44.62 per cent.
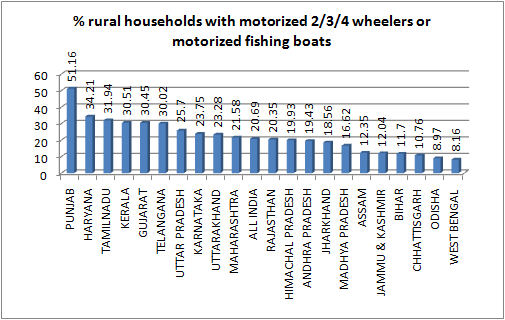
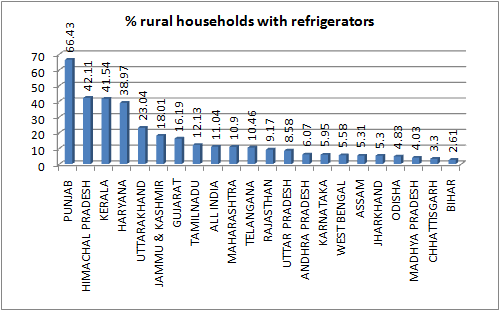
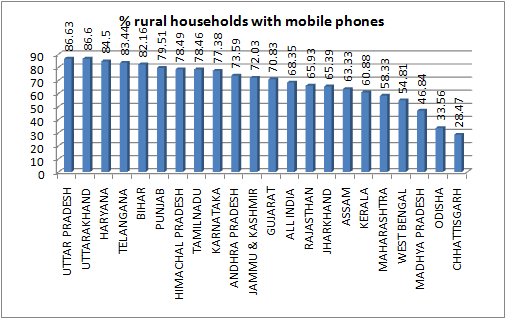
8. Despite poor income levels, Gujarat has highest number of rural households which own at least a two-wheeler motorized vehicle — 30.45 per per cent. This is against the all-India average of 20.69 per cent.9. Gujarat’s 16.19 per cent of rural households own refrigerators, as against the all-India average of 11.04 per cent.10. Despite claims of Gujarat having one of the best communications network in India, 70.83 per cent or rural households have mobile phones, almost equal to the all-India average of 68.35 per cent.11. Gujarat’s 25.8 per cent of the rural households own no communications network, neither mobile nor telephone, again around the same as the all-India average — 27.93 per cent.—
Sourced on SECC, charts have been prepared to make inter-state comparison by selecting 21 major Indian states. For more details, click HERE







Comments