Noteban triggered mass corruption, 75-82% Indians sold Rs 500 and 1000 notes for less than Rs 400 and 900: Survey
By A Representative
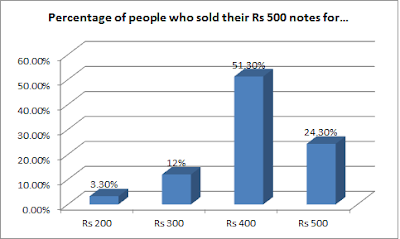
A civil society survey, carried out in January-February 2017, but released now, has revealed that only 24.3 percent of the respondents said that they were able to exchange their banned Rs 500 notes “for the same amount”, while 75 percent reported that “an old Rs 500 note was sold for Rs 400 or less in valid currency.”
Carried out by Act Now for Harmony and Democracy (ANHAD) in alliance with 32 people’s organizations spread out in 21 Indian states, and involving 3,647 respondents, the survey, seeking to ascertain the behaviour of the people during the demonetization or noteban period, November-December 2016, further pointed out that of those who said that they received Rs 400 or less amount for Rs 500 note, 51.3 percent reported it was exchanged for Rs 400, 12 reported they exchanged it for Rs 300, and 3.3 percent reported that the Rs 500 note was exchanged for as low as Rs 200.
Among the respondents, about 25 percent of respondents were students, 13.7 percent unemployed, 18 percent employed in private sector, 10 percent working as 'labour', 4.9 percent reported household work as their profession, 3.4 were in government job and 4.4 percent were involved in agriculture.
The percentage of those who reported 'Hindu' was 65.0 and 'Muslims' were about 27.0 percent – constituting together about 92 percent. There were about 3 percent of Christians and about 2 percent were Sikh. About 3 percent said that they do not follow any religion or said humanity is their religion.
Caste-wise distribution showed that about 37 percent belonged to the general category, 29 percent were SC/ST and 30.7 percent belonged to OBC. Then, 80 percent said they had access to television, 29 percent listened to radio, 50 percent read newspapers, and so on.
The report, which has been published in a new book, “Demonetization: Exorcising the ‘Demon’”, released to mark one year of the surprise Modi government announcement to withdraw from circulation Rs 500 and Rs 1,000 notes, said, “Region-wise distribution showed that this form of corruption was rampant in all the regions.”
 Pointing out that the “industry to exchange old notes cropped up overnight across the country”, the report said, “The fate of the banned Rs 1,000 note was not very different”, adding, though, that here “the percentage of those who said that they exchanged their Rs 1,000 note for the same amount without any reduction was reduced to 17.4 percent.”
Pointing out that the “industry to exchange old notes cropped up overnight across the country”, the report said, “The fate of the banned Rs 1,000 note was not very different”, adding, though, that here “the percentage of those who said that they exchanged their Rs 1,000 note for the same amount without any reduction was reduced to 17.4 percent.”
A civil society survey, carried out in January-February 2017, but released now, has revealed that only 24.3 percent of the respondents said that they were able to exchange their banned Rs 500 notes “for the same amount”, while 75 percent reported that “an old Rs 500 note was sold for Rs 400 or less in valid currency.”
Carried out by Act Now for Harmony and Democracy (ANHAD) in alliance with 32 people’s organizations spread out in 21 Indian states, and involving 3,647 respondents, the survey, seeking to ascertain the behaviour of the people during the demonetization or noteban period, November-December 2016, further pointed out that of those who said that they received Rs 400 or less amount for Rs 500 note, 51.3 percent reported it was exchanged for Rs 400, 12 reported they exchanged it for Rs 300, and 3.3 percent reported that the Rs 500 note was exchanged for as low as Rs 200.
Among the respondents, about 25 percent of respondents were students, 13.7 percent unemployed, 18 percent employed in private sector, 10 percent working as 'labour', 4.9 percent reported household work as their profession, 3.4 were in government job and 4.4 percent were involved in agriculture.
The percentage of those who reported 'Hindu' was 65.0 and 'Muslims' were about 27.0 percent – constituting together about 92 percent. There were about 3 percent of Christians and about 2 percent were Sikh. About 3 percent said that they do not follow any religion or said humanity is their religion.
Caste-wise distribution showed that about 37 percent belonged to the general category, 29 percent were SC/ST and 30.7 percent belonged to OBC. Then, 80 percent said they had access to television, 29 percent listened to radio, 50 percent read newspapers, and so on.
The report, which has been published in a new book, “Demonetization: Exorcising the ‘Demon’”, released to mark one year of the surprise Modi government announcement to withdraw from circulation Rs 500 and Rs 1,000 notes, said, “Region-wise distribution showed that this form of corruption was rampant in all the regions.”
 Pointing out that the “industry to exchange old notes cropped up overnight across the country”, the report said, “The fate of the banned Rs 1,000 note was not very different”, adding, though, that here “the percentage of those who said that they exchanged their Rs 1,000 note for the same amount without any reduction was reduced to 17.4 percent.”
Pointing out that the “industry to exchange old notes cropped up overnight across the country”, the report said, “The fate of the banned Rs 1,000 note was not very different”, adding, though, that here “the percentage of those who said that they exchanged their Rs 1,000 note for the same amount without any reduction was reduced to 17.4 percent.”
The report said, “More than 82 percent of the respondents reported that in their locality, a Rs 1,000 note was sold for less than Rs 900”, adding, 40.7 percent respondents “reported that the note was sold for Rs 800” .
Then, “those who said they exchanged their note for Rs 700 were 9.2 percent, those who reported Rs 600 was the price of a Rs 1000 note were 4 percent, and 4.8 percent said that an old Rs 1,000 note was sold at as low as Rs 500.”
The report noted, “Region-wise distribution showed that more than 90 percent respondents witnessed reduction of cost of Rs 1,000 note in Central (98%) and Northern (91.4%) regions”, adding, astonishingly, “10.4 percent of the respondents said that in their locality a Rs 1,000 note was sold for as low as Rs 100.”
The report commented, “It is quite evident that the claim made by the Prime Minister that the objective of demonetization was to clean Indian economy of black money was hollow. Instead, a new channel for generating black money opened up."
The report noted, “Region-wise distribution showed that more than 90 percent respondents witnessed reduction of cost of Rs 1,000 note in Central (98%) and Northern (91.4%) regions”, adding, astonishingly, “10.4 percent of the respondents said that in their locality a Rs 1,000 note was sold for as low as Rs 100.”
The report commented, “It is quite evident that the claim made by the Prime Minister that the objective of demonetization was to clean Indian economy of black money was hollow. Instead, a new channel for generating black money opened up."
It added, "It can be concluded that a very large amount of legitimately earned money by the poor citizens was converted into black money. With one stroke the people's toil and labour was devalued.”

Comments