By Jag Jivan*
Fresh data released by the National Sample Survey Organization (NSSO) in the report “Household Consumer Expenditure across Socio-Economic Groups” have suggested the purchasing power of the three socially disadvantaged groups – scheduled tribes (STs), scheduled castes (SCs) and other backward classes (OBCs) – in Gujarat is considerably less than what prevails in most of the Indian states, especially in the rural areas. Calculated as monthly per capita expenditure (MPCE), purchasing power figures are based on NSSO’s survey in 2011-12. The report was released in February 2015.
Fresh data released by the National Sample Survey Organization (NSSO) in the report “Household Consumer Expenditure across Socio-Economic Groups” have suggested the purchasing power of the three socially disadvantaged groups – scheduled tribes (STs), scheduled castes (SCs) and other backward classes (OBCs) – in Gujarat is considerably less than what prevails in most of the Indian states, especially in the rural areas. Calculated as monthly per capita expenditure (MPCE), purchasing power figures are based on NSSO’s survey in 2011-12. The report was released in February 2015.
In Gujarat’s rural areas, the STs’ average MPCE is Rs 1,155, which is less than 12 out of 20 major Indian states (Punjab, Himachal Pradesh, Kerala, Jammu & Kashmir, Haryana, Uttarakhand, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Assam, Tamil Nadu, Rajasthan and Maharashtra). The SCs’ average MPCE is Rs 1,374, which is less than 11 major states (Kerala, Punjab, Jammu & Kashmir, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Uttarakhand, Karnataka and Rajasthan). And the OBCs’ average MPCE is Rs 1,582, which is less than 11 major Indian states (Kerala, Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Rajasthan, Maharashtra, Uttarakhand, Karnataka).
The pattern also suggests the obvious detail, that the STs’ purchasing power in rural India, as in Gujarat, is considerably less than the other two disadvantaged groups, SCs and OBCs.
As for “Others” in rural Gujarat – mainly consisting of upper castes – their average MPCE, at Rs 1,988, is found to be not just higher than the three disadvantaged groups. It is also higher than all 20 major states but five – Kerala (Rs 3,156), Punjab (Rs 3,009), Haryana (Rs 2,531), Himachal Pradesh (Rs 2,255), and Rajasthan (Rs 2,119).
As for “Others” in rural Gujarat – mainly consisting of upper castes – their average MPCE, at Rs 1,988, is found to be not just higher than the three disadvantaged groups. It is also higher than all 20 major states but five – Kerala (Rs 3,156), Punjab (Rs 3,009), Haryana (Rs 2,531), Himachal Pradesh (Rs 2,255), and Rajasthan (Rs 2,119).
The comparative data significantly suggest that all three disadvantaged groups in rural, STs, SCs and OBCs, are worse off than majority of other major states, but this is not the case with upper castes.
As for Gujarat’s urban areas, the pattern is quite different from the one that is prevailing in rural Gujarat. Here, STs’ and OBCs’ MPCE is worse than majority of Indian states, but this is not true for SCs.
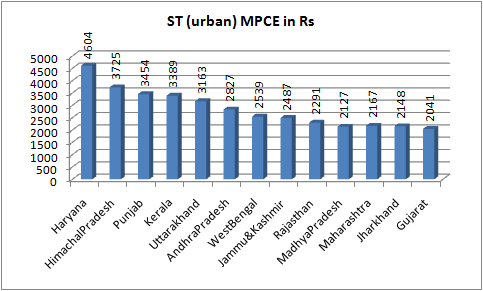
Comparative figures suggest that STs’ MPCE in urban Gujarat at Rs 2,014 is less than 12 other states (Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Kerala, Uttarakhand, Andhra Pradesh, West Bengal, Jammu & Kashmir, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra and Jharkhand). This would possibly suggest that tribal migrants in urban areas, mainly working at construction sites, are more ill-paid in Gujarat than most of India.
As for Gujarat’s urban areas, the pattern is quite different from the one that is prevailing in rural Gujarat. Here, STs’ and OBCs’ MPCE is worse than majority of Indian states, but this is not true for SCs.
Comparative figures suggest that STs’ MPCE in urban Gujarat at Rs 2,014 is less than 12 other states (Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Kerala, Uttarakhand, Andhra Pradesh, West Bengal, Jammu & Kashmir, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra and Jharkhand). This would possibly suggest that tribal migrants in urban areas, mainly working at construction sites, are more ill-paid in Gujarat than most of India.
As for SCs, their MPCE is quite high in urban Gujarat – Rs 2,359 – compared to most of the 20 major states but three (Himachal Pradesh, Maharashtra and Kerala). Presumably, this could be because a big section of Dalits living in the urban areas work in government of semi-government offices, with many of them able to gain from the reservation policy.
Interestingly, the urban Gujarat OBCs’ MPCE – Rs 2,086 – is not only less than that of the SCs but is only a little higher than the STs (Rs 2,014). Also, the urban Gujarat OBCs’ MPCE is lower than 12 other states (Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Maharashtra, Kerala, Haryana, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Punjab, Andhra Pradesh, Assam, West Bengal and Rajasthan).
Interestingly, the urban Gujarat OBCs’ MPCE – Rs 2,086 – is not only less than that of the SCs but is only a little higher than the STs (Rs 2,014). Also, the urban Gujarat OBCs’ MPCE is lower than 12 other states (Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Maharashtra, Kerala, Haryana, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Punjab, Andhra Pradesh, Assam, West Bengal and Rajasthan).
Those in the “Others” category in urban Gujarat, belonging to the upper castes, evidently, have a much higher MPCE (Rs 2,946) as compared to STs, SCs and OBCs. Yet, it is lower than eight other states– Kerala (Rs 5,376), Haryana (Rs 4,669), Karnataka (Rs 4,378), Maharashtra (Rs 3,699), Himachal Pradesh (Rs 3,329), Punjab (Rs 3,209), Andhra Pradesh Rs (3,080), and Chhattisgarh (Rs 2,980).
---
*Freelance writer






Comments