By A Representative
The latest National Sample Survey Organisation (NSSO) report, “Key Indicators of Urban Slums in India”, released in December 2013 and based on survey the top statistical body carried out in the second half of 2012, has once again suggested that Gujarat’s slums are one of the worst in India insofar as providing basic infrastructural facilities are concerned. Rajiv Shah takes a closer look at the report:
While Gujarat’s slums, numbering 2,923 (both notified and non-notified), form 8.72 per cent of all slums in the country (33,510), the three states with higher number of slums than Gujarat are Maharashtra (7,723), Andhra Pradesh (3,956) and West Bengal (3957). Despite a relatively higher number, what is particularly appalling is, Gujarat slums fail to score better than most states whether it is pucca houses, tapped water, electricity, pucca roads, latrines, drainage, or garbage disposal.
While the survey results do not show a complete all-India picture, as results of only in a dozen states of India – Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Gujarat, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Odisha, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh and West Bengal – have been made public, even then there is reason for worry for Gujarat’s policy makers, who recently came up with a new slum policy in order to encourage private developers to “develop” the slum areas. There is a distinct view that the policy gives lip service to in situ slum development, but actually gives huge concessions to private developers in the form of extra floor space index (FSI) elsewhere or free open space for constructing commercial residential blocks left free after constructing houses for the slum dwellers.
While Gujarat’s slums, numbering 2,923 (both notified and non-notified), form 8.72 per cent of all slums in the country (33,510), the three states with higher number of slums than Gujarat are Maharashtra (7,723), Andhra Pradesh (3,956) and West Bengal (3957). Despite a relatively higher number, what is particularly appalling is, Gujarat slums fail to score better than most states whether it is pucca houses, tapped water, electricity, pucca roads, latrines, drainage, or garbage disposal.
While the survey results do not show a complete all-India picture, as results of only in a dozen states of India – Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Gujarat, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Odisha, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh and West Bengal – have been made public, even then there is reason for worry for Gujarat’s policy makers, who recently came up with a new slum policy in order to encourage private developers to “develop” the slum areas. There is a distinct view that the policy gives lip service to in situ slum development, but actually gives huge concessions to private developers in the form of extra floor space index (FSI) elsewhere or free open space for constructing commercial residential blocks left free after constructing houses for the slum dwellers.
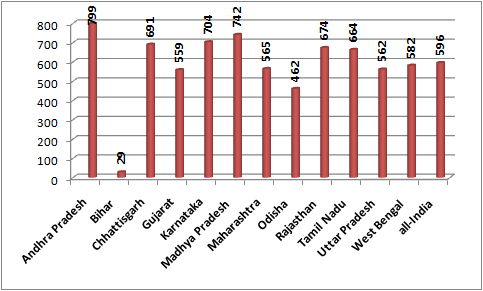 |
Proportion pucca houses (per 1000) |
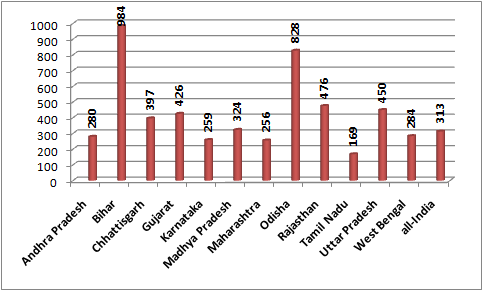 |
Proportion of slums without latrines (per 1000) |
 |
| Proportion of slums without power (per 1000) |
 |
Proportion of slums without drainage (per 1000) |
 |
| Proportion of slums facing waterlogging due to rainfall (per 1000) |
Significantly, while the policy takes care of “notified slums”, which aren’t many in numbers in Gujarat, it fails to address slum-dwellers of the non-notified slum areas, which form nearly 90 per cent of all slums of the state. These non-notified slums are nobody’s baby, as they have mostly cropped up with fast pace of urbanization; they may be on government or private land. In Gujarat, 44.1 per cent of the slums are situated on private land, which is equal to the all-India average. While the NSSO generally refrains from commenting on individual states, at one place it notes that garbage disposal is a major problem in Gujarat slums. It says, “The proportion of non-notified slums without any garbage disposal arrangement was as high as 89 per cent in Rajasthan, 83 per cent in Bihar, and over 60 per cent in Odisha, Chhattisgarh and Gujarat.” It only goes to suggest that several progressive states have a better garbage disposal facility in slums than Gujarat.
The situation was found to be no better in other sectors. In Gujarat, 55.9 per cent of the slum households have pucca houses, which is less than the national average of 59.6 per cent. Of the dozen states surveyed, the states which have lesser number of households than Gujarat with pucca houses are Bihar (a mere 2.9 per cent) and Odisha 46.2 per cent. All other states, including poorer Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh, have a higher proportion of households with pucca houses. While counting households, the NSSO said, “Any compact settlement with a collection of poorly built tenements, mostly of temporary nature, crowded together, usually with inadequate sanitary and drinking water facilities in unhygienic conditions, was considered a slum by the survey, provided at least 20 households lived there.”
The situation can be said to be particularly bad, as 31.9 per cent of the slums in Gujarat have been covered under the Government of India’s flagship Jawaharlal Nehru National Urban Renewal Mission (JNNURM), which is higher than most states except Andhra Pradesh (40.2 per cent) and West Bengal (43.0 per cent). Gujarat’s 80.1 per cent of the slums have access to tapped drinking water, provided by corporation, municipality, other local body, public or private authority. Here, the national average is 71.4 per cent, which is much lower than Gujarat’s, states with higher proportion of slums with tapped water are Chhattisgarh (88.5 per cent), Karnataka 94.8 per cent), Maharashtra (80.1 per cent), and Tamil Nadu (97.3 per cent). While drinking water may not be a major issue, electricity indeed is found to be one, with 8.4 per cent of the slums not having any power, as against the all-India average of 6.5 per cent. The states with higher proportion of slums without power are Maharashtra (9.6 per cent), Rajasthan (26.8 per cent) and Uttar Pradesh (16.1 per cent).
Then, 53.7 per cent of Gujarat’s slums have pucca roads, as against the national average of 66.1 per cent. The states with lesser percentage of slums having pucca roads are Odisha (30.0 per cent) and Bihar (30.7 per cent). Further, 42.6 per cent of Gujarat’s slums do not have any of latrines, as against the national average of 31.3 per cent. The states with higher percentage of slums without latrines are Bihar (98.4 per cent), Odisha (82.8 per cent), Rajasthan (47.6 per cent) and Uttar Pradesh (45.0 per cent). Also, 42.7 per cent of Gujarat’s slums do not have any drainage facility, as against the all-India average of 30.9 per cent. The states with higher proportion of slums without drainage are Chhattisgarh (65.8 per cent) and Odisha (56.0 per cent). And finally, 61.2 per cent of Gujarat slums suffer from water logging during rainfall, as against the national average of just 31.6 per cent.
Noting some salient features of the survey, the NSSO says, a total of 881 slums – 441 notified and 440 non-notified – were surveyed. The issues taken up included (a) number of slums and slumdwelling households, and (b) proportions of slums possessing specific desirable and undesirable characteristics. The number of slums in urban India was estimated at 33,510 – 13,761 notified and 19,749 non-notified. The number of slum-dwelling households was estimated at 8.8 million – about 5.6 million in notified and 3.2 million in non-notified slums.
The NSSO adds, “The average number of households per slum was 263. The percentage of slums lacking facilities considered necessary for a decent urban life varied widely across states and was higher in non-notified slums, as in case of latrine facility (absent in 16 per cent of notified and 42 per cent of non-notified slums), drainage facility (absent in 11 per cent of notified and 45 per cent of non-notified slums), garbage disposal arrangement (absent in 11 per cent of notified and 38 per cent of non-notified slums), and electricity (absent in 0.1 per cent of notified and 11 per cent of non-notified slums).”
The situation can be said to be particularly bad, as 31.9 per cent of the slums in Gujarat have been covered under the Government of India’s flagship Jawaharlal Nehru National Urban Renewal Mission (JNNURM), which is higher than most states except Andhra Pradesh (40.2 per cent) and West Bengal (43.0 per cent). Gujarat’s 80.1 per cent of the slums have access to tapped drinking water, provided by corporation, municipality, other local body, public or private authority. Here, the national average is 71.4 per cent, which is much lower than Gujarat’s, states with higher proportion of slums with tapped water are Chhattisgarh (88.5 per cent), Karnataka 94.8 per cent), Maharashtra (80.1 per cent), and Tamil Nadu (97.3 per cent). While drinking water may not be a major issue, electricity indeed is found to be one, with 8.4 per cent of the slums not having any power, as against the all-India average of 6.5 per cent. The states with higher proportion of slums without power are Maharashtra (9.6 per cent), Rajasthan (26.8 per cent) and Uttar Pradesh (16.1 per cent).
Then, 53.7 per cent of Gujarat’s slums have pucca roads, as against the national average of 66.1 per cent. The states with lesser percentage of slums having pucca roads are Odisha (30.0 per cent) and Bihar (30.7 per cent). Further, 42.6 per cent of Gujarat’s slums do not have any of latrines, as against the national average of 31.3 per cent. The states with higher percentage of slums without latrines are Bihar (98.4 per cent), Odisha (82.8 per cent), Rajasthan (47.6 per cent) and Uttar Pradesh (45.0 per cent). Also, 42.7 per cent of Gujarat’s slums do not have any drainage facility, as against the all-India average of 30.9 per cent. The states with higher proportion of slums without drainage are Chhattisgarh (65.8 per cent) and Odisha (56.0 per cent). And finally, 61.2 per cent of Gujarat slums suffer from water logging during rainfall, as against the national average of just 31.6 per cent.
Noting some salient features of the survey, the NSSO says, a total of 881 slums – 441 notified and 440 non-notified – were surveyed. The issues taken up included (a) number of slums and slumdwelling households, and (b) proportions of slums possessing specific desirable and undesirable characteristics. The number of slums in urban India was estimated at 33,510 – 13,761 notified and 19,749 non-notified. The number of slum-dwelling households was estimated at 8.8 million – about 5.6 million in notified and 3.2 million in non-notified slums.
The NSSO adds, “The average number of households per slum was 263. The percentage of slums lacking facilities considered necessary for a decent urban life varied widely across states and was higher in non-notified slums, as in case of latrine facility (absent in 16 per cent of notified and 42 per cent of non-notified slums), drainage facility (absent in 11 per cent of notified and 45 per cent of non-notified slums), garbage disposal arrangement (absent in 11 per cent of notified and 38 per cent of non-notified slums), and electricity (absent in 0.1 per cent of notified and 11 per cent of non-notified slums).”



Comments