By Udaya S Mishra, Srinivas Goli*
Economic growth in India for last two decades has been impressive excluding a few of odd years. However, the translation of economic growth into quality of human welfare is still debatable.
Economic growth in India for last two decades has been impressive excluding a few of odd years. However, the translation of economic growth into quality of human welfare is still debatable.
A first step in this direction began when an alternative yardstick of measuring development moved from Gross Domestic Product (GDP -- a money metric measure of a country’s economy) to human development (comprising of means and ends together).
Despite this shift, measuring quality of human welfare has not entirely replaced the measurement of economic progress (mostly assessed in GDP terms). Contentions surrounding GDP has been its uncertain capacity to translate means to ends along with inclusiveness and sustainability feature. Even the Human Development Index remains inadequate to accommodate these features.
On recognition of this limitation there has been efforts at assessment of human welfare with alternative comprehensive measures that go beyond the means and accommodate ends as well. An effort in this direction has been the formulation of social progress index that comprehends three dimensions namely basic human needs, foundations of wellbeing and opportunity described by 89 indicators.
This exercise of measuring social progress is in place since 2011 and it offers an account of social progress for 168 countries of the world. The fresh edition of this index in 2022 places India at 110th rank and at fourth tier of performance.
Despite this shift, measuring quality of human welfare has not entirely replaced the measurement of economic progress (mostly assessed in GDP terms). Contentions surrounding GDP has been its uncertain capacity to translate means to ends along with inclusiveness and sustainability feature. Even the Human Development Index remains inadequate to accommodate these features.
On recognition of this limitation there has been efforts at assessment of human welfare with alternative comprehensive measures that go beyond the means and accommodate ends as well. An effort in this direction has been the formulation of social progress index that comprehends three dimensions namely basic human needs, foundations of wellbeing and opportunity described by 89 indicators.
This exercise of measuring social progress is in place since 2011 and it offers an account of social progress for 168 countries of the world. The fresh edition of this index in 2022 places India at 110th rank and at fourth tier of performance.
Despite being at this tier of performance India’s progress has been commendable with a gain of 8.49 points realising a score of 60.19/100. On the same account compared to 5.4 points gain at the global level, India’s progress is faster.
India shows quantum jump in domains like basic needs, access to information communication, water sanitation, shelter and health wellness. However, the gains in many other components has been quite slow and in fact negative in domains like environmental quality, personal rights and inclusiveness.
A review of social progress levels within the country and its states generates six tiers ranging an index value between 43 and 66. According to this classification, the states at the lowest tier are Assam, Bihar and Jharkhand with an index value between 43 and 45 (see Figure 1).
In contrast, the first tier of states that have an index value of 62 to 66 include the two south Indian state of Kerala and Tamil Nadu along with a few smaller states and union territories. In fact, this index across districts of India suggest that districts with poor social progress are concentrated largely in states like Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and Madhya Pradesh.
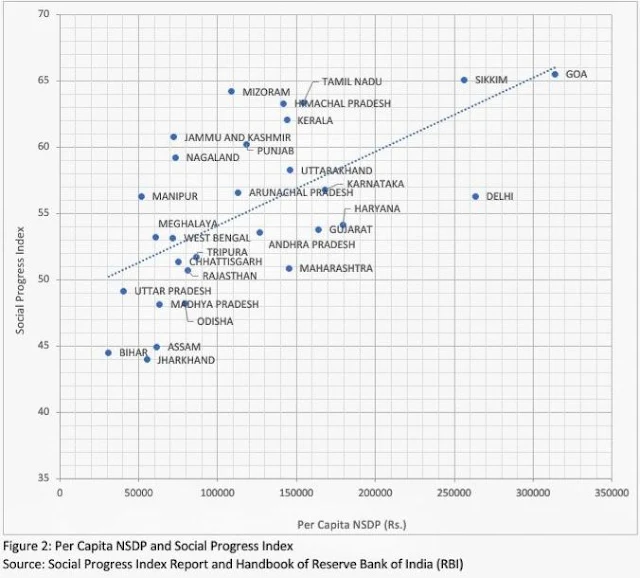
Reading the relationship between economic growth and social progress across the states of India is perplexing. For some of the states and union territories, we observe a positive relationship between the social progress index and per capita NSDP (Net State Domestic Product -- a monetary measure of state level economic development) implying that they are able to convert their economic progress into better social outcomes.
For example, Goa and Sikkim rank high in this regard, while Bihar ranks the lowest on both economic and social progress. However, some states and UTs, such as Delhi, have high per capita NSDP but relatively low social progress, and vice-versa. Kerala and Tamil Nadu are two large states having a greater translation value of their economic progress into social progress.
Another striking takeaway from the trends in social progress index and the per capita NSDP over time is that the number of outliers have increased from that in 2017 to 2022 (see Figure 1 and Figure 2).
India shows quantum jump in domains like basic needs, access to information communication, water sanitation, shelter and health wellness. However, the gains in many other components has been quite slow and in fact negative in domains like environmental quality, personal rights and inclusiveness.
A review of social progress levels within the country and its states generates six tiers ranging an index value between 43 and 66. According to this classification, the states at the lowest tier are Assam, Bihar and Jharkhand with an index value between 43 and 45 (see Figure 1).
In contrast, the first tier of states that have an index value of 62 to 66 include the two south Indian state of Kerala and Tamil Nadu along with a few smaller states and union territories. In fact, this index across districts of India suggest that districts with poor social progress are concentrated largely in states like Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and Madhya Pradesh.
Reading the relationship between economic growth and social progress across the states of India is perplexing. For some of the states and union territories, we observe a positive relationship between the social progress index and per capita NSDP (Net State Domestic Product -- a monetary measure of state level economic development) implying that they are able to convert their economic progress into better social outcomes.
For example, Goa and Sikkim rank high in this regard, while Bihar ranks the lowest on both economic and social progress. However, some states and UTs, such as Delhi, have high per capita NSDP but relatively low social progress, and vice-versa. Kerala and Tamil Nadu are two large states having a greater translation value of their economic progress into social progress.
Another striking takeaway from the trends in social progress index and the per capita NSDP over time is that the number of outliers have increased from that in 2017 to 2022 (see Figure 1 and Figure 2).
This indicates that gains in the economic growth have been unable to translate into social progress for some states, while in others relatively lower levels of economic development have coincided with a higher social progress index. This highlights the need for more effective social welfare policies to achieve the aspired levels of social progress among the several states.
The measure of social progress involves a wide range of indicators which are a subset of many of the SDG indicators that qualify this index as a holistic measure of human welfare compared with existing set of alternative indices that evaluates human welfare. Social progress therefore should be the yardstick of monitoring progress in human well-being in this day and time.
---
*Udaya S Mishra is Professor and Srinivas Goli is Associate Professor with the International Institute for Population Sciences, Mumbai
The measure of social progress involves a wide range of indicators which are a subset of many of the SDG indicators that qualify this index as a holistic measure of human welfare compared with existing set of alternative indices that evaluates human welfare. Social progress therefore should be the yardstick of monitoring progress in human well-being in this day and time.
---
*Udaya S Mishra is Professor and Srinivas Goli is Associate Professor with the International Institute for Population Sciences, Mumbai



Comments