By Srinivas Goli, Shreya Singh*
The Assam government’s recent efforts towards addressing child marriages in the state appears to be doing more harm than good. Recent weeks have witnessed a brutal crackdown on culprits identified under the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act (POCSO, 2012) and Prevention of Child Marriages Act (PCMA, 2006) in the state of Assam. So far over several thousand arrested under PCMA. Supposedly driven by the underage marriage rate estimate provided by the National Family Health Survey (NFHS)-5 released in 2022, the government claims to continue this exercise till the next state elections of 2026.
News reports are rife with incidences of teens bleeding to death during childbirth or committing suicide to evade their parents’ or husbands’ arrests. Dread and dismay pervade the state as young mothers are rendered helpless in the face of sudden arrests of their husbands, who are in most cases, the sole breadwinners of their households. Clearly, the legislative actions of the state have served to only worsen the situation.
A viable reason for this is that mere legislative action, that too ex post facto, breeds a sense of fear and helplessness, inducing individuals to conceal and adopt illegal means in order to evade being arrested.
If the cause of concern motivating this legislative frenzy are high maternal mortality ratios and teenage pregnancy rates, then emphasis should be laid upon providing access to contraception and maternal health care, increasing education, providing job opportunities and financial independence to women. Enabling provisions such as these provide women with the agency to exercise personal choice, bodily autonomy and postpone births to higher ages.
Moreover, teenage pregnancies, maternal and infant mortality are not solely driven by age at marriage. The cause and effect relationship of child marriage and maternal and child health outcomes are more complex than stated. They are responses to a variety of factors at play, the most prominent of which is poverty and lack of access to education. In fact, age at marriage itself is determined by the poverty and lack of access to education. Below, we have explained some of these issues in detail.
Under this uncertain circumstance, inadequate access to education for children and coupled with poverty makes them vulnerable to marry off young girls get rid of burden and also as a matter of protection and safety. And, location of Muslims in such poverty-stricken locations is higher compared to Hindus.
Although, religion-wise differences in child marriage rates are greater in Assam compared to other states, it is difficult to say religion in itself is causing child marriage. If religion is the major reason for child marriage, why the situation is different in Jammu and Kashmir, Kerala and Uttar Pradesh and other states. The presentation of National Family Health Survey data in Figure 1 suggest that child marriage rates among Hindus is more compared to Muslims in Jammu and Kashmir.
From Figure 2, we found a strong correlation between no schooling and child marriage rates across the districts of Assam. Similarly, the percentage of woman had teenage birth in Assam is about six times higher among no schooling mothers compared to those who are 12 or more years of schooling.
For instance, Figure 3 suggest lack of a minimum of 10 years of schooling results in poor maternal health care uptake, while from the Figure 2, it is evident that child marriage is positively associated with the lack of schooling.
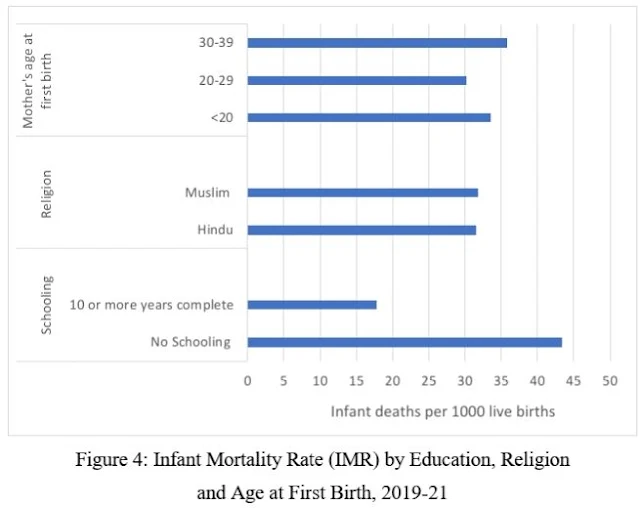
Furthermore, a careful observation of the infant mortality rate (IMR) prevalence in Figure 4 for the state of Assam suggest that the differences by schooling several times higher compared to the differences by mother’s age at first birth and religion.
Careful study of the data suggests that legal measures such as PCMA can make marriages clustering around 18 or just after crossing 18 years. And, marriage after reaching 18 years of age is not a magic milestone which results into socio-economic and health outcomes for women and their children.
However, exercising harsh legal arms to curb down child marriages retrospectively, plunges women into further throes of deprivation, trapping an entire generation into a vicious cycle of poverty and compromise seeking essential social safety programmes including maternal and child health care services. Moreover, existing law on PCMA doesn’t support its retrospective application.
Once a marriage is consummated, the law considers it to be valid and children born out of such unions enjoy all legal rights. It is imperative that the focus shifts back to improving women’s access to education, job opportunities, contraception and maternal and child health care services for better holistic socio-economic and health outcomes and draw a way to each sustainable development goals.
---
*Srinivas Goli is associate professor, International Institute for Population Sciences, Mumbai; Shreya Singh is student, International Institute for Population Sciences, Mumbai. A version of this article was first published in The Wire
The Assam government’s recent efforts towards addressing child marriages in the state appears to be doing more harm than good. Recent weeks have witnessed a brutal crackdown on culprits identified under the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act (POCSO, 2012) and Prevention of Child Marriages Act (PCMA, 2006) in the state of Assam. So far over several thousand arrested under PCMA. Supposedly driven by the underage marriage rate estimate provided by the National Family Health Survey (NFHS)-5 released in 2022, the government claims to continue this exercise till the next state elections of 2026.
News reports are rife with incidences of teens bleeding to death during childbirth or committing suicide to evade their parents’ or husbands’ arrests. Dread and dismay pervade the state as young mothers are rendered helpless in the face of sudden arrests of their husbands, who are in most cases, the sole breadwinners of their households. Clearly, the legislative actions of the state have served to only worsen the situation.
A viable reason for this is that mere legislative action, that too ex post facto, breeds a sense of fear and helplessness, inducing individuals to conceal and adopt illegal means in order to evade being arrested.
If the cause of concern motivating this legislative frenzy are high maternal mortality ratios and teenage pregnancy rates, then emphasis should be laid upon providing access to contraception and maternal health care, increasing education, providing job opportunities and financial independence to women. Enabling provisions such as these provide women with the agency to exercise personal choice, bodily autonomy and postpone births to higher ages.
Moreover, teenage pregnancies, maternal and infant mortality are not solely driven by age at marriage. The cause and effect relationship of child marriage and maternal and child health outcomes are more complex than stated. They are responses to a variety of factors at play, the most prominent of which is poverty and lack of access to education. In fact, age at marriage itself is determined by the poverty and lack of access to education. Below, we have explained some of these issues in detail.
What is causing child marriage in Assam
Research demonstrates that the reasons for child marriage in India are heterogeneous across the states. In case of Assam, cultural factors play a key role along-side poverty and lack of access to education. Assam along with parts of West Bengal have precarious, uncertain and unsustainable livelihoods primarily attributable to factors specific to local geographies. Communities often mobile and comprise huge migrant population.Under this uncertain circumstance, inadequate access to education for children and coupled with poverty makes them vulnerable to marry off young girls get rid of burden and also as a matter of protection and safety. And, location of Muslims in such poverty-stricken locations is higher compared to Hindus.
Although, religion-wise differences in child marriage rates are greater in Assam compared to other states, it is difficult to say religion in itself is causing child marriage. If religion is the major reason for child marriage, why the situation is different in Jammu and Kashmir, Kerala and Uttar Pradesh and other states. The presentation of National Family Health Survey data in Figure 1 suggest that child marriage rates among Hindus is more compared to Muslims in Jammu and Kashmir.
From Figure 2, we found a strong correlation between no schooling and child marriage rates across the districts of Assam. Similarly, the percentage of woman had teenage birth in Assam is about six times higher among no schooling mothers compared to those who are 12 or more years of schooling.
Does child marriage is the sole reason for poor maternal and child health outcomes?
Child marriage certainly deepens the problems of poor and lower educated women, especially in terms of maternal and child health outcomes. However, the mechanisms through which child marriage affects socio-economic and health outcomes of women and their children are more complex.For instance, Figure 3 suggest lack of a minimum of 10 years of schooling results in poor maternal health care uptake, while from the Figure 2, it is evident that child marriage is positively associated with the lack of schooling.
Furthermore, a careful observation of the infant mortality rate (IMR) prevalence in Figure 4 for the state of Assam suggest that the differences by schooling several times higher compared to the differences by mother’s age at first birth and religion.
Way forward
The Assam government’s recent efforts towards addressing child marriages in the state through legal means and force are doing more harm than good. Such futile legislative crackdown, worsening vulnerabilities of those who already suffering from extreme poverty, illiteracy and poor maternal health outcomes.Careful study of the data suggests that legal measures such as PCMA can make marriages clustering around 18 or just after crossing 18 years. And, marriage after reaching 18 years of age is not a magic milestone which results into socio-economic and health outcomes for women and their children.
However, exercising harsh legal arms to curb down child marriages retrospectively, plunges women into further throes of deprivation, trapping an entire generation into a vicious cycle of poverty and compromise seeking essential social safety programmes including maternal and child health care services. Moreover, existing law on PCMA doesn’t support its retrospective application.
Once a marriage is consummated, the law considers it to be valid and children born out of such unions enjoy all legal rights. It is imperative that the focus shifts back to improving women’s access to education, job opportunities, contraception and maternal and child health care services for better holistic socio-economic and health outcomes and draw a way to each sustainable development goals.
---
*Srinivas Goli is associate professor, International Institute for Population Sciences, Mumbai; Shreya Singh is student, International Institute for Population Sciences, Mumbai. A version of this article was first published in The Wire





Comments