
By Rajiv Shah
The All-India Survey on Higher Education (AISHE), operating under the Ministry of Human Resource Development, Government of India, in its recent report has suggested that Gujarat’s gross enrollment ratio (GER) in higher education, which was 21.3 per cent of the population in the age group 18-23 in 2010-11, went down to 17.6 per cent a year later – in 2011-12. Worse, Gujarat’s GER ranking fell from ninth among 20 major states in 2010-11 to 13th in 2011-12. The AISHE report also indicates that while Gujarat’s GER performance was above national average (19.4 per cent of the population in the 18-23 age group) in 2010-11, in 2011-12, the GER nationally improved to 20.4 per cent, which pushed Gujarat below the national average.
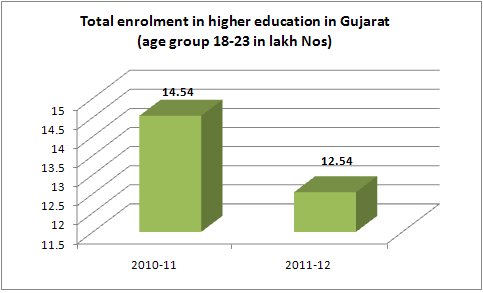
In absolute terms, the AISHE data suggest, in Gujarat, in 2011-12, a total of 12,54,202 students in the age group 18-23 were enrolled in higher education, of which 7,31,241 were boys and 5,22,961 girls. Significantly, this was down from the enrollment in 2010-11, when a total of 14,53,726 students in this age group were enrolled – 8,47,044 of them boys and 6,06,682 girls. This happened at a time when, at the national level, total enrolment went up from 2,74,99,749 (1,54,66,559 boys and 1,20,33,190 girls) in 2010-11 to 2,85,62,693 (1,58,74,800 boys and 1,26,87,893 girls) in 2011-12.

The All-India Survey on Higher Education (AISHE), operating under the Ministry of Human Resource Development, Government of India, in its recent report has suggested that Gujarat’s gross enrollment ratio (GER) in higher education, which was 21.3 per cent of the population in the age group 18-23 in 2010-11, went down to 17.6 per cent a year later – in 2011-12. Worse, Gujarat’s GER ranking fell from ninth among 20 major states in 2010-11 to 13th in 2011-12. The AISHE report also indicates that while Gujarat’s GER performance was above national average (19.4 per cent of the population in the 18-23 age group) in 2010-11, in 2011-12, the GER nationally improved to 20.4 per cent, which pushed Gujarat below the national average.
In absolute terms, the AISHE data suggest, in Gujarat, in 2011-12, a total of 12,54,202 students in the age group 18-23 were enrolled in higher education, of which 7,31,241 were boys and 5,22,961 girls. Significantly, this was down from the enrollment in 2010-11, when a total of 14,53,726 students in this age group were enrolled – 8,47,044 of them boys and 6,06,682 girls. This happened at a time when, at the national level, total enrolment went up from 2,74,99,749 (1,54,66,559 boys and 1,20,33,190 girls) in 2010-11 to 2,85,62,693 (1,58,74,800 boys and 1,26,87,893 girls) in 2011-12.

AISHE report suggests that, in 2011-12, Tamil Nadu had the best GER with 38.2 per cent, followed by Haryana 27.2 per cent, Andhra Pradesh 27.6 per cent, Maharashtra 27.4 per cent, Himachal Pradesh 25 per cent, Karnataka 24 per cent, Jammu & Kashmir 23.7 per cent, Kerala 23.1 per cent, Punjab 20 per cent, Rajasthan 18 per cent, and Gujarat 17.6 per cent. Mainly of the so-called Bimaru states performed worse than Gujarat – Madhya Pradesh 17.4 per cent, UP 16.8 per cent, Odisha 16.3 per cent, Assam 14.4 per cent, Bihar 13.1 per cent, West Bengal 12.8 per cent, Chhattisgarh 11 per cent, and Jharkhand 8.4 per cent.
Girls’ enrolment in higher education further suggests neglect of the girl child in the age group 18-23 in Gujarat. In Gujarat, the female GER in higher education in the age group 18-23 was 15.7 per cent in 2011-12, which is down from 18.8 per cent GER in 2010-11. The national GER for girls in higher education in 2011-12 was three percentage points better than Gujarat’s – 18.9 per cent. In 2011-12, as many as 12 states witnessed a better GER for girls in higher education than Gujarat – the best being Tamil Nadu with 35.2 per cent, followed by Uttarakhand, Haryana, Kerala, Jammu & Kashmir, Maharashtra, Himachal Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Uttar Pradesh and Punjab.

Not without reason, the gender parity index in higher education in Gujarat, according to the AISHE report, was 0.81 (or 81 girls against every 100 boys) in 2011-12, which is less than the national average of 0.88. And, instead of improving, it has shown a downward trend – in 2010-11 the gender parity ratio in higher education Gujarat was 0.80. Gujarat’s GER in 2011-12, in fact, was worse than such “poor” states such as Assam (0.98), Jharkhand (0.84), and Chhattisgarh (0.82), not to talk of states which are considered progressive – Kerala (.139), Haryana (0.96), Himachal Pradesh (0.94), Karnataka (0.90), Tamil Nadu (0.86), and Maharashtra (0.84).
Though the Gujarat government claims that higher education in the state has been expanding, figures suggests that, in Gujarat, there are 25 colleges per lakh population in the age group 18-23, equal to the all-India average. This is lower than several states, including Andhra Pradesh (48 colleges), Karnataka (44 colleges), Himachal Pradesh (38 colleges), Haryana (33 colleges), Maharashtra (34 colleges), Rajasthan 32 colleges, Uttarakhand (32 colleges), Kerala (30 colleges) and Tamil Nadu (30 colleges).

Though the Gujarat government claims that higher education in the state has been expanding, figures suggests that, in Gujarat, there are 25 colleges per lakh population in the age group 18-23, equal to the all-India average. This is lower than several states, including Andhra Pradesh (48 colleges), Karnataka (44 colleges), Himachal Pradesh (38 colleges), Haryana (33 colleges), Maharashtra (34 colleges), Rajasthan 32 colleges, Uttarakhand (32 colleges), Kerala (30 colleges) and Tamil Nadu (30 colleges).

It is ironical that the AISHE report has been released at a time when Gujarat has, over the last five years, been stressing excessively on skill development and technical education, claiming itself to an all-India model for other states to follow. It even got a report prepared by a Government of India agency, National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC), titled “District wise skill gap study for the State of Gujarat (2012-17, 2017-22)” in order to identify the type of skills that the state would need at a time when “Gujarat has emerged as industrial agglomerate”. The NSDC employed top international consultants, KPMG, to do the job for Gujarat. KPMG has worked as consultants with the state government to promote industrial investment for several years.
Even as praising lack of skills, according to the KPMG, has led to a situation where there is an “in-ward migration” from other states into Gujarat. For instance, it says, “Non-availability of skilled professionals for ship-building and ship-breaking industries forces industrial units to acquire skilled professionals from southern states like Tamil Nadu.” It adds, while an even higher proportion of workers come as groups from Uttar Pradesh and Bihar as contract workers for working in the industry in Gujarat, there is a need for “adequate skilling of local youth in related segments” in order to “provide local employment opportunities.”

Even as praising lack of skills, according to the KPMG, has led to a situation where there is an “in-ward migration” from other states into Gujarat. For instance, it says, “Non-availability of skilled professionals for ship-building and ship-breaking industries forces industrial units to acquire skilled professionals from southern states like Tamil Nadu.” It adds, while an even higher proportion of workers come as groups from Uttar Pradesh and Bihar as contract workers for working in the industry in Gujarat, there is a need for “adequate skilling of local youth in related segments” in order to “provide local employment opportunities.”

According to KPMG estimates, an additional increase in incremental manpower requirement during XII plan (2012-17) and XIII plan (2017-22) periods will be 3 million and 2.65 million. “Significant portion of the new jobs created, especially in agri-allied activities (0.42 million during XII Plan), construction (0.26 million during XII Plan), trade and retail (0.21 million during XII Plan) and textiles (0.16 million during XII Plan) would witness mere realignment of workforce displaced from agriculture — due to the expected impact of mechanization on cultivation activities”, the KPMG believes.
Underlining lack of trained manpower in Gujarat, the KPMG says, “In order to promote economic and industrial development in a state, the essential requirement is the capacity to develop skilled manpower of good quality in adequate number.” It adds, “Gujarat being an industrially developed state with significant opportunities for organized employment, there is an ever increasing need for graduates and skilled professionals.”
“While Gujarat has a marginally better penetration of higher education compared to national average, other progressive knowledge economies like Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and Karnataka have higher penetration than Gujarat”, the KPMG says, adding, “Low affordability for private education in rural areas is the key reason for limited interest from private players. Government policies on capacity creation have been traditionally based on population prorate basis in a region. This has resulted in limited capacities across rural areas leading to fewer graduating students due to either non-enrollment in higher education or high drop-out rate at the school level.”
“While Gujarat has a marginally better penetration of higher education compared to national average, other progressive knowledge economies like Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and Karnataka have higher penetration than Gujarat”, the KPMG says, adding, “Low affordability for private education in rural areas is the key reason for limited interest from private players. Government policies on capacity creation have been traditionally based on population prorate basis in a region. This has resulted in limited capacities across rural areas leading to fewer graduating students due to either non-enrollment in higher education or high drop-out rate at the school level.”

Comments