By Rajiv Shah
Latest official figures suggest that “model” Gujarat appears to be competing with Left-ruled Kerala in the spike in illegal mining cases. One of the top four Indian states which have witnessed a spike in illegal mining cases in 2017, Gujarat saw a 28.1% rise in illegal cases in a year, from 6,499 to 8,325, as against Kerala’s saw of a 31.34% rise from from 3,701 to 4,861.
The other two states, which saw a rise in illegal mining cases are Madhya Pradesh, by 1.86%, from 13,627 to 13,880, and Rajasthan 7.76%, from 3,661 to 3,945.
The data further show that, between 2010 and 2017, while “model” Gujarat saw 41,699 illegal mining cases, the rise over the years has been stupendous. In 2009, in Gujarat, 4,020 illegal mining cases were reported, which rose to 8,325, a whopping 107.09% rise.
The report also reveals that of Gujarat’s 6,499 illegal mining cases reported in 2016, FIRs were lodged in just 84 cases.
Revealing this, an authoritative report, based in data provided in Parliament, says, “Mining is considered illegal when it is done without a license or outside the licensed area and when more than the permissible amount is extracted.”
Coming down heavily on illegal mining, the Supreme Court in August 2017, had said that mining companies, which operated without environmental clearance, should pay compensation equivalent to 100% of the value of the minerals extracted illegally. Following the verdict, in February 2018, the apex court quashed all 88 mining leases in Goa 'hastily' renewed by the state government in 2015 to "benefit private mining leaseholders".
Pointing out that these “these developments point to poor governance and resource management across the country”, the report, authored by Lalit Maurya, Sobhojit Goswami and Isha Bajpai, says, if one takes into account illegal mining cases since 2009, Maharashtra “tops the list of states”, witnessing a “28 per cent increase from 26,283 in 2009-10 to 33,621 in 2015-16.”
Latest official figures suggest that “model” Gujarat appears to be competing with Left-ruled Kerala in the spike in illegal mining cases. One of the top four Indian states which have witnessed a spike in illegal mining cases in 2017, Gujarat saw a 28.1% rise in illegal cases in a year, from 6,499 to 8,325, as against Kerala’s saw of a 31.34% rise from from 3,701 to 4,861.
The other two states, which saw a rise in illegal mining cases are Madhya Pradesh, by 1.86%, from 13,627 to 13,880, and Rajasthan 7.76%, from 3,661 to 3,945.
The data further show that, between 2010 and 2017, while “model” Gujarat saw 41,699 illegal mining cases, the rise over the years has been stupendous. In 2009, in Gujarat, 4,020 illegal mining cases were reported, which rose to 8,325, a whopping 107.09% rise.
The report also reveals that of Gujarat’s 6,499 illegal mining cases reported in 2016, FIRs were lodged in just 84 cases.
Revealing this, an authoritative report, based in data provided in Parliament, says, “Mining is considered illegal when it is done without a license or outside the licensed area and when more than the permissible amount is extracted.”
Coming down heavily on illegal mining, the Supreme Court in August 2017, had said that mining companies, which operated without environmental clearance, should pay compensation equivalent to 100% of the value of the minerals extracted illegally. Following the verdict, in February 2018, the apex court quashed all 88 mining leases in Goa 'hastily' renewed by the state government in 2015 to "benefit private mining leaseholders".
Pointing out that these “these developments point to poor governance and resource management across the country”, the report, authored by Lalit Maurya, Sobhojit Goswami and Isha Bajpai, says, if one takes into account illegal mining cases since 2009, Maharashtra “tops the list of states”, witnessing a “28 per cent increase from 26,283 in 2009-10 to 33,621 in 2015-16.”
Interestingly, according to the report, published in the top environmental journal “Down to Earth”, in December 2017, despite rise in illegal mining, the Government of India proposed giving more power to states to grant environmental clearance, which suggests it was seeking to shed responsibility.
The report insists, “While the intention may be to decentralise the process of environmental clearance, capacity and accountability remain a problem. State-level clearance authorities neither have the capacity to handle increased work load, nor is there a system of accountability in place to ensure transparency in how clearances are issued.”
Against this backdrop, the report regrets, “Mining in India is a scam bigger than 2G and Commonwealth Games but has failed to catch people's attention because of difficulty in linking it with big political names, its eventual beneficiaries. It is difficult to estimate the loss to public exchequer because of illegal mining across states.”
Pointing out that since 2009, Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, Rajasthan and Tamil Nadu are the only four states that have registered a decline in illegal mining, the report states, “With a drop in 5,827 illegal mining cases since 2009-10, Andhra Pradesh has fared the best among all states when it comes to numbers.”
It adds, “However, Odisha has covered maximum ground by reducing the number of cases by more than 90 per cent, from 487 in 2009-10 to just 45 in 2016-17.”
The report also points to the fact that West Bengal has seen more than 400% increase in illegal mining from 113 cases in 2009-10 to 575 in 2015-16, and Jharkhand saw a massive surge in illegal mining between 2009-10 and 2015-16 from just 15 to 1,645.
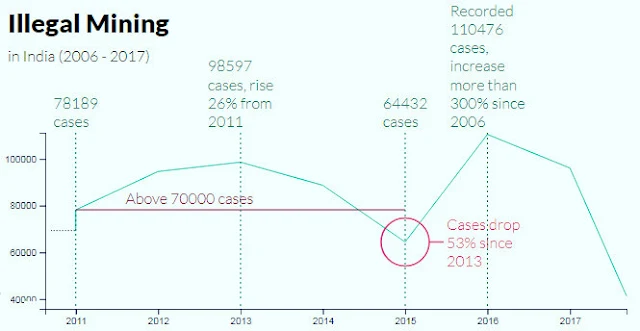
At the same time, the report states, 2015-16 has so far been the worst year during this seven-year period with the nationwide illegal mining cases witnessing a sharp spike from 69,316 in 2009-10 to 110,476”, adding, “Uttar Pradesh, which reached its peak during 2015-16 (11,575 cases), brought the number of cases down to 5,737 within a year.”
The report further says, “Within a year, Haryana managed to reduce illegal mining cases by more than 66%. In 2015-16, it had 3,912 cases, which came down to 1,345 in 2016-17. Jharkhand stood second in achieving this feat by registering more than 50 per cent decrease -- from 1,645 in 2015-16 to 694 in 2016-17.”
The report states, “India, one of the world's largest producers and exporters of mica, coal, iron ore, bauxite and manganese, has long been grappling with illegal mining, primarily in Karnataka, Goa, Haryana, Rajasthan and Odisha, ever since it opened up mining to private companies in the 1990s.”
It adds, “From soil erosion and groundwater contamination to loss of forest cover and biodiversity, unbridled mining plays havoc with an ecosystem. But despite this, prosecution rate is very low in such cases.”
“For example”, the report notes, “Maharashtra recorded 1,39,706 illegal mining cases between 2013 and 2017 -- the highest in the country -- but only 712 first information reports (FIR) and one court case were filed.”
Against this backdrop, the report regrets, “Mining in India is a scam bigger than 2G and Commonwealth Games but has failed to catch people's attention because of difficulty in linking it with big political names, its eventual beneficiaries. It is difficult to estimate the loss to public exchequer because of illegal mining across states.”
Pointing out that since 2009, Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, Rajasthan and Tamil Nadu are the only four states that have registered a decline in illegal mining, the report states, “With a drop in 5,827 illegal mining cases since 2009-10, Andhra Pradesh has fared the best among all states when it comes to numbers.”
It adds, “However, Odisha has covered maximum ground by reducing the number of cases by more than 90 per cent, from 487 in 2009-10 to just 45 in 2016-17.”
The report also points to the fact that West Bengal has seen more than 400% increase in illegal mining from 113 cases in 2009-10 to 575 in 2015-16, and Jharkhand saw a massive surge in illegal mining between 2009-10 and 2015-16 from just 15 to 1,645.
At the same time, the report states, 2015-16 has so far been the worst year during this seven-year period with the nationwide illegal mining cases witnessing a sharp spike from 69,316 in 2009-10 to 110,476”, adding, “Uttar Pradesh, which reached its peak during 2015-16 (11,575 cases), brought the number of cases down to 5,737 within a year.”
The report further says, “Within a year, Haryana managed to reduce illegal mining cases by more than 66%. In 2015-16, it had 3,912 cases, which came down to 1,345 in 2016-17. Jharkhand stood second in achieving this feat by registering more than 50 per cent decrease -- from 1,645 in 2015-16 to 694 in 2016-17.”
The report states, “India, one of the world's largest producers and exporters of mica, coal, iron ore, bauxite and manganese, has long been grappling with illegal mining, primarily in Karnataka, Goa, Haryana, Rajasthan and Odisha, ever since it opened up mining to private companies in the 1990s.”
It adds, “From soil erosion and groundwater contamination to loss of forest cover and biodiversity, unbridled mining plays havoc with an ecosystem. But despite this, prosecution rate is very low in such cases.”
“For example”, the report notes, “Maharashtra recorded 1,39,706 illegal mining cases between 2013 and 2017 -- the highest in the country -- but only 712 first information reports (FIR) and one court case were filed.”


Comments