 |
By Rajiv Shah
In an important revelation, the National Sample Survey Organization (NSSO) report, “Employment and unemployment situation among social groups in India”, released in January 2015, has suggested that Gujarat is one of the few states which has failed to be effective in providing guaranteed job to those seeking it in the rural areas under the National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (NREGA). The survey, carried out in 2011-12, finds that, in Gujarat, a total of 17.2 per cent rural persons registered themselves and got job cards under NREGA. However, these as many as 29.2 per cent failed to get any employment despite the fact that NREGA is a job guarantee scheme for 100 days to anyone in the rural areas seeking it. It is noteworthy that the all-India average of persons refused job under NREGA is considerably less — it is 18.8 per cent. The percentage of failure to provide job to the jobseekers in Gujarat was higher than most major Indian states, except four – Maharashtra 44.8 per cent, Bihar 35.4 per cent, Karnataka 30.5 per cent and Punjab 30.4 per cent.
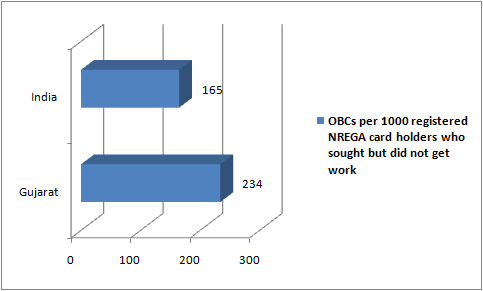
The survey further finds that situation in Gujarat in providing jobs under NREGA was equally bad vis-à-vis most of India for all social groups, except for scheduled castes (SCs). Thus, the survey data shows, 32.4 per cent scheduled tribes (STs) in Gujarat received job cards to work under NREGA. Of this, 34.9 per cent failed to get a “guaranteed job”. This is against the all-India average of 19 per cent. As for SCs, of the 22.5 per cent rural persons seeking job, 18.1 per cent failed to get it in Gujarat. This is against the all-India average of 20.4 per cent. Then, of 15.5 per cent other backward class (OBC) rural persons seeking job in Gujarat, 23.4 per cent failed to get it, against the all-India average of 16.5 per cent. Finally, in the “Others” category, in Gujarat, just about 1.9 per cent rural persons were found to be seeking job, but of this 46 per cent failed to get it, as against the all-India average of 21.9 per cent.
In an important revelation, the National Sample Survey Organization (NSSO) report, “Employment and unemployment situation among social groups in India”, released in January 2015, has suggested that Gujarat is one of the few states which has failed to be effective in providing guaranteed job to those seeking it in the rural areas under the National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (NREGA). The survey, carried out in 2011-12, finds that, in Gujarat, a total of 17.2 per cent rural persons registered themselves and got job cards under NREGA. However, these as many as 29.2 per cent failed to get any employment despite the fact that NREGA is a job guarantee scheme for 100 days to anyone in the rural areas seeking it. It is noteworthy that the all-India average of persons refused job under NREGA is considerably less — it is 18.8 per cent. The percentage of failure to provide job to the jobseekers in Gujarat was higher than most major Indian states, except four – Maharashtra 44.8 per cent, Bihar 35.4 per cent, Karnataka 30.5 per cent and Punjab 30.4 per cent.
The survey further finds that situation in Gujarat in providing jobs under NREGA was equally bad vis-à-vis most of India for all social groups, except for scheduled castes (SCs). Thus, the survey data shows, 32.4 per cent scheduled tribes (STs) in Gujarat received job cards to work under NREGA. Of this, 34.9 per cent failed to get a “guaranteed job”. This is against the all-India average of 19 per cent. As for SCs, of the 22.5 per cent rural persons seeking job, 18.1 per cent failed to get it in Gujarat. This is against the all-India average of 20.4 per cent. Then, of 15.5 per cent other backward class (OBC) rural persons seeking job in Gujarat, 23.4 per cent failed to get it, against the all-India average of 16.5 per cent. Finally, in the “Others” category, in Gujarat, just about 1.9 per cent rural persons were found to be seeking job, but of this 46 per cent failed to get it, as against the all-India average of 21.9 per cent.
 |
Explaining its methodology the report states, “For persons of age 18 years and above of the rural households having NREGA job cards, information was collected on whether the person was registered in any NREGS job card, and if registered, whether worked in NREGA works during last 365 days in terms of the three types of responses viz. ‘worked’, ‘sought but did not get work’ and ‘did not seek work’. A person was considered to have worked in NREGA works during last 365 days if he/she had worked for at least for one day in GNREGA works during last 365 days.”
The report finds that, in the country as a whole, “38.4 per cent of the households in rural areas had NREGA job cards and a higher proportion of households belonging to ST or SC category had NREGA job cards than OBC or others category of households: 57.2 per cent of ST households and 50 per cent of SC households had NREGA job cards compared to 34.2 per cent of OBC households and 27.1 per cent of others category of households.” The survey found that, at the all-India average, the “number of job cards issued per 1000 of job card holder households of rural India was the highest among OBC households – nearly 1224 job cards were issued per 1000 OBC households with NREGA job cards while number of job cards issued per 1000 households with NREGA job cards were 1185 for ST, 1177 for SC and 1174 for others category of households.”
The report finds that, in the country as a whole, “38.4 per cent of the households in rural areas had NREGA job cards and a higher proportion of households belonging to ST or SC category had NREGA job cards than OBC or others category of households: 57.2 per cent of ST households and 50 per cent of SC households had NREGA job cards compared to 34.2 per cent of OBC households and 27.1 per cent of others category of households.” The survey found that, at the all-India average, the “number of job cards issued per 1000 of job card holder households of rural India was the highest among OBC households – nearly 1224 job cards were issued per 1000 OBC households with NREGA job cards while number of job cards issued per 1000 households with NREGA job cards were 1185 for ST, 1177 for SC and 1174 for others category of households.”
 |
As for “proportion of persons of age 18 years and above registered in NREGA job cards”, the report states, it “varied across social groups.” Thus, “it was the highest, nearly 42.6 per cent for persons belonging to ST households, followed by 30.9 per cent for SC, 21 per cent for OBC, and the lowest 14.7 per cent for persons in others category of households.” The report further says, “It is seen that a higher proportion of males of age 18 years and above were registered in NREGA job cards compared to females across all the social groups: it was 48.3 per cent for males compared to 37.1 per cent for females among ST, 36.6 per cent for males compared 25.2 per cent for females for SC, 24.2 per cent for males compared to 17.9 per cent for females for OBC and 19.8 per cent for males compared to 9.5 per cent for females for others category.”
Then, the report states, “In rural areas, among persons of age 18 years and above registered in NREGA job cards, 50.5 per cent got work, 18.8 per cent sought but did not get MGNREG work, and 30.5 per cent did not seek work in NERGA work. Proportion of persons of age 18 years and above registered in NREGA work who got work in NREGA work was the highest among SC (55.6 per cent), followed by ST (50.5 per cent), OBC (49.1 per cent) and was the lowest among others category (45.5 per cent). Among persons of age 18 years and above and registered in MGNREG job card, the proportion of persons who sought but did not get work in NREGA work was the highest for others (21.9 per cent) and it was the lowest among OBC (16.5 per cent) while it was 19 per cent among ST and 20.4 per cent among SC.”
Then, the report states, “In rural areas, among persons of age 18 years and above registered in NREGA job cards, 50.5 per cent got work, 18.8 per cent sought but did not get MGNREG work, and 30.5 per cent did not seek work in NERGA work. Proportion of persons of age 18 years and above registered in NREGA work who got work in NREGA work was the highest among SC (55.6 per cent), followed by ST (50.5 per cent), OBC (49.1 per cent) and was the lowest among others category (45.5 per cent). Among persons of age 18 years and above and registered in MGNREG job card, the proportion of persons who sought but did not get work in NREGA work was the highest for others (21.9 per cent) and it was the lowest among OBC (16.5 per cent) while it was 19 per cent among ST and 20.4 per cent among SC.”
 |
At a time when the Government of India has decided to stick around with NREGA after earlier decision to water it down, with the latest Union budget suggesting an increase in allocation for it, there should be some concern to at the policy level as to why Gujarat is failing to perform well to provide guaranteed jobs to the rural poor. In fact, reports suggest massive corruption in Gujarat in implementing NREGA, which could be a reason why so many people seeking guaranteed job are failing to get one. Recently, the state government admitted in the Gujarat state assembly that rampant was corruption in the implementation of NREGA, and in Sabarkantha district, it has been forced to launch an inquiry after it received nine complaints. The state government reply came to a question by Ashwin Kotwal, representing in the assembly from Khedbrahma constituency in Sabarkantha district of North Gujarat.
Indifference in implementing NREGA has been taken seriously by the Gujarat High Court as well. In February 2014, the High Court issued a notice to the state government over a petition filed by the Gujarat Mazdoor Sabha challenging the state government’s decision of terminating services of Gram Rojgar Sevak (GRS) and other technical staff under the NREGA. The state government sought explanation about this from the state government. The employees’ union moved the High Court after the state government passed a notification to discontinue the services of GRS and other technical staff.
Indifference in implementing NREGA has been taken seriously by the Gujarat High Court as well. In February 2014, the High Court issued a notice to the state government over a petition filed by the Gujarat Mazdoor Sabha challenging the state government’s decision of terminating services of Gram Rojgar Sevak (GRS) and other technical staff under the NREGA. The state government sought explanation about this from the state government. The employees’ union moved the High Court after the state government passed a notification to discontinue the services of GRS and other technical staff.
Comments