Flopped model? 8 states officially "beat" Gujarat's decelerating growth rate; five states in per capita income
By A Representative
Gujarat’s Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) for the year 2014-15 has been “officially” released – it has been calculated to be 7.70 per cent at constant prices, taking 2011-12 as the base year. The figures, released by the Government of India’s Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MOSPI), show, it is the lowest growth over the last three years.
In the year 2012-13, Gujarat’s growth rate was 10.84 per cent, which went down to 8.31 per cent in 2013-14.
While the figures for the year 2015-16 have still not been officially released, experts have calculated that they would be 6.7 per cent, lower than the all-India average of 7.6 per cent. The calculation is based on Gujarat government estimates of current price GSDP (without deducting deduction), pegged at 10 per cent, lowest since 2010-11.
Gujarat’s Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) for the year 2014-15 has been “officially” released – it has been calculated to be 7.70 per cent at constant prices, taking 2011-12 as the base year. The figures, released by the Government of India’s Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MOSPI), show, it is the lowest growth over the last three years.
In the year 2012-13, Gujarat’s growth rate was 10.84 per cent, which went down to 8.31 per cent in 2013-14.
While the figures for the year 2015-16 have still not been officially released, experts have calculated that they would be 6.7 per cent, lower than the all-India average of 7.6 per cent. The calculation is based on Gujarat government estimates of current price GSDP (without deducting deduction), pegged at 10 per cent, lowest since 2010-11.
Interestingly, eight major Indian states out of 21 have registered a higher rate of growth than Gujarat – providing ammunition to critics to declare that the state's neo-liberal economic growth model, projected by Prime Minister Narendra Modi for the country as a whole, is beginning to falter.
The highest growth rate for 2014-15 was registered by Bihar at 15.56 per cent, followed by Jharkhand (11.04 per cent), Telangana (8.82 per cent), Tamil Nadu (8.65 per cent), Andhra Pradesh (7.98 per cent), Haryana (7.98 per cent), and Chhattisgarh (7.85 per cent).
So far, only four major states have declared their GSDP estimates for the year 2015-16 – Andhra Pradesh (10.99 per cent), Bihar (10.27 per cent), Madhya Pradesh (10.16 per cent), Telangana (9.24 per cent), Karnataka (7.79 per cent), and Uttarakhand (7.65 per cent).
In per capita rate of growth, too, there is deceleration, the MOSPI figures show. At Rs 1,08,433 for the year 2014-15, the figures show that the growth rate was 6.80 per cent, down from 7.09 per cent in 2013-14 and 10.48 per cent in 2012-13.
The highest growth rate for 2014-15 was registered by Bihar at 15.56 per cent, followed by Jharkhand (11.04 per cent), Telangana (8.82 per cent), Tamil Nadu (8.65 per cent), Andhra Pradesh (7.98 per cent), Haryana (7.98 per cent), and Chhattisgarh (7.85 per cent).
So far, only four major states have declared their GSDP estimates for the year 2015-16 – Andhra Pradesh (10.99 per cent), Bihar (10.27 per cent), Madhya Pradesh (10.16 per cent), Telangana (9.24 per cent), Karnataka (7.79 per cent), and Uttarakhand (7.65 per cent).
In per capita rate of growth, too, there is deceleration, the MOSPI figures show. At Rs 1,08,433 for the year 2014-15, the figures show that the growth rate was 6.80 per cent, down from 7.09 per cent in 2013-14 and 10.48 per cent in 2012-13.
While Gujarat’s per capita income is higher than the national average (Rs 72,889), five major states registered a higher per capita income than Gujarat – Haryana (Rs 1,24,092), Uttarakhand (Rs 1,20,759), Kerala (Rs 1,15,225), Tamil Nadu (Rs 1,13,817), and Maharashtra (Rs 1,13,817).
Notably, according to neo-liberal economists, one of whom is currently Gujarat government’s top man in the policy-making body, Niti Aayog, Arvind Panagariya, economic growth in the economy should automatically take care of the need for improvement in social sectors, a theory disputed by a wide range of economists, one of whom is Nobel laureate Amartya Sen.
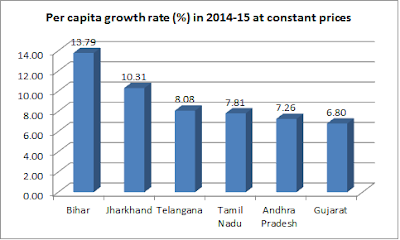
Gujarat’s per capita rate of growth at 6.80 per cent in 2014-15, say MOSPI data, is lower than five other states – Bihar (13.79 per cent), Jharkhand (10.31 per cent), Talangana (8.08 per cent), Tamil Nadu (7.81 per cent) and Andhra Pradesh (7.16 per cent).
Notably, according to neo-liberal economists, one of whom is currently Gujarat government’s top man in the policy-making body, Niti Aayog, Arvind Panagariya, economic growth in the economy should automatically take care of the need for improvement in social sectors, a theory disputed by a wide range of economists, one of whom is Nobel laureate Amartya Sen.
Gujarat’s per capita rate of growth at 6.80 per cent in 2014-15, say MOSPI data, is lower than five other states – Bihar (13.79 per cent), Jharkhand (10.31 per cent), Talangana (8.08 per cent), Tamil Nadu (7.81 per cent) and Andhra Pradesh (7.16 per cent).



Comments