By Rajiv Shah
Will the new report by well-known elite NGO Toxics Link create a ripple in the powerful corridors of Delhi? Titled “Quantitative analysis of microplastics along River Ganga”, forwarded to Counterview, doesn’t just say that Ganga is the second most polluted river in the world, next only to Yangtze (China). It goes ahead to do a comparison of microplastics pollution in three cities shows Varanasi – the Lok Sabha constituency of Prime Minister Narendra Modi – is more polluted compared to Kanpur and Haridwar.
Referring to a study in “Nature Communications”, the The Toxics link report says, “The study estimated that between 1.15 and 2.41 million tonnes of plastic waste currently enters the ocean every year from rivers. Globally 74% of marine pollution is contributed by the top 20 polluting rivers, mostly Asian rivers. The Ganga is the 2nd most polluted river....”
The report adds, “According to the study, the Ganga is the second largest contributing catchment with an annual discharge of 0.12 million tonnes of plastic. It has also observed that the river’s midpoint input estimates peak in August (wet season) with 44,500 tonnes while the river discharges <150 tonnes per month between December and March (dry season).”The report says, the 2,525 km long Ganges contributes “315 tonnes of plastic waste per day, the equivalent of 79 elephants”, regretting – indeed without referring to Modi’s big talk that “It's my destiny to serve Maa Ganga” – that “despite campaigns for cleanliness, the country has not been able to control the massive proliferation of plastics along the Ganga.”
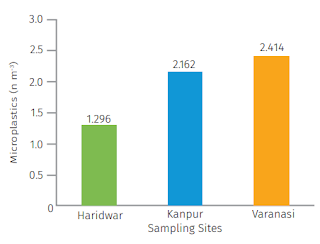
Coming to microplastics, the report says, spot samples in the three cities “indicated higher microplastic levels in the samples collected from Kanpur and Varanasi in comparison to Haridwar”, underlining, “Among the three cities, Varanasi showed the maximum load of microplastics in the Ganga waters as compared to the other two cities.”
Pointing out that this may be due to “cumulative downstream pollution as well as industry and human activities”, the report says, “Assi Ghat in Varanasi had the maximum abundance of microplastics, which may be due to the drainage of sewage and industrial effluents directly into the Ganga.”
The report underlines, “The concern of microplastic pollution in the Ganga is critical as the water from the river is used for drinking and irrigation purposes quite extensively. An increased abundance of microplastics in a river increases the potential harm that it can cause to organisms and humans. After ingestion, microplastics cause toxicity through several pathways and mechanisms.”
Pointing out that the “polymeric compounds and additives such as copper ions used in the production of plastics are toxic”, the report adds, “More importantly, microplastics absorb various toxins in waters (including harmful chemicals) that are first absorbed onto microplastics, and subsequently may desorb inside a host organism.”
At each of the three cities, Toxics Link experts collected a set of five surface water samples with a focus on sampling areas which were heavily polluted with any wastewater treatment plant along the river.
As for Kanpur, the number of microplastics detected in the surface water samples of river Ganga was 2.16±0.500 Mps/m3, “slightly low concentration of microplastics was found in this region as compared to Varanasi”, the report says, adding, “Haridwar resulted in the lowest number of MPs/m3 (1.30±0.518) as compared to Varanasi and Kanpur.”
Will the new report by well-known elite NGO Toxics Link create a ripple in the powerful corridors of Delhi? Titled “Quantitative analysis of microplastics along River Ganga”, forwarded to Counterview, doesn’t just say that Ganga is the second most polluted river in the world, next only to Yangtze (China). It goes ahead to do a comparison of microplastics pollution in three cities shows Varanasi – the Lok Sabha constituency of Prime Minister Narendra Modi – is more polluted compared to Kanpur and Haridwar.
Referring to a study in “Nature Communications”, the The Toxics link report says, “The study estimated that between 1.15 and 2.41 million tonnes of plastic waste currently enters the ocean every year from rivers. Globally 74% of marine pollution is contributed by the top 20 polluting rivers, mostly Asian rivers. The Ganga is the 2nd most polluted river....”
The report adds, “According to the study, the Ganga is the second largest contributing catchment with an annual discharge of 0.12 million tonnes of plastic. It has also observed that the river’s midpoint input estimates peak in August (wet season) with 44,500 tonnes while the river discharges <150 tonnes per month between December and March (dry season).”The report says, the 2,525 km long Ganges contributes “315 tonnes of plastic waste per day, the equivalent of 79 elephants”, regretting – indeed without referring to Modi’s big talk that “It's my destiny to serve Maa Ganga” – that “despite campaigns for cleanliness, the country has not been able to control the massive proliferation of plastics along the Ganga.”
Coming to microplastics, the report says, spot samples in the three cities “indicated higher microplastic levels in the samples collected from Kanpur and Varanasi in comparison to Haridwar”, underlining, “Among the three cities, Varanasi showed the maximum load of microplastics in the Ganga waters as compared to the other two cities.”
Pointing out that this may be due to “cumulative downstream pollution as well as industry and human activities”, the report says, “Assi Ghat in Varanasi had the maximum abundance of microplastics, which may be due to the drainage of sewage and industrial effluents directly into the Ganga.”
The report underlines, “The concern of microplastic pollution in the Ganga is critical as the water from the river is used for drinking and irrigation purposes quite extensively. An increased abundance of microplastics in a river increases the potential harm that it can cause to organisms and humans. After ingestion, microplastics cause toxicity through several pathways and mechanisms.”
Pointing out that the “polymeric compounds and additives such as copper ions used in the production of plastics are toxic”, the report adds, “More importantly, microplastics absorb various toxins in waters (including harmful chemicals) that are first absorbed onto microplastics, and subsequently may desorb inside a host organism.”
At each of the three cities, Toxics Link experts collected a set of five surface water samples with a focus on sampling areas which were heavily polluted with any wastewater treatment plant along the river.
Especially referring to Varanasi, the report says, “The number of microplastics detected in surface water of river Ganga in Varanasi was (2.42±0.405 MPs/m3 )... Assi Ghat showed the maximum abundance of microplastics as it is the most popular ghat in Varanasi and is one of the very few ghats that is linked with the city through a wide street.”
“Additionally”, the report says, “One sewage outlet was observed draining the wastewater and sewage directly into the Ganga which may affect the microplastics concentration and abundance in and around the sampling site. The second most polluted ghat was Kedareshwer ghat followed by Dasaswamedha and Sheetala ghat.”As for Kanpur, the number of microplastics detected in the surface water samples of river Ganga was 2.16±0.500 Mps/m3, “slightly low concentration of microplastics was found in this region as compared to Varanasi”, the report says, adding, “Haridwar resulted in the lowest number of MPs/m3 (1.30±0.518) as compared to Varanasi and Kanpur.”




Comments