 |
A recent Gujarat government affidavit says that as non-Muslim minorities’ plight was not considered by the Sachar Committee, it is “unconstitutional”. First, this is factually incorrect. And secondly, latest data suggest Muslims in India generally fall in the category of backward sections of population, and other minorities are much better off.
In a recent affidavit to the Supreme Court, the Gujarat government has said that “the Sachar Committee is neither constitutional nor statutory.” Explaining its position, it insisted, the committee “has not taken into consideration other religious communities, i.e. Sikhs, Christians, Buddhists and Parsis. Therefore, it cannot form the basis of the scheme.” It added, “The committee’s target was to help the Muslims only.” The affidavit was the Gujarat government’s response to the Government of India’s (GoI’s) stand on Gujarat’s refusal to implement the pre-matriculation minority scholarship scheme. Gujarat moved the apex court against Gujarat High Court verdict ratifying the scholarship scheme meant for students belonging to five religious minorities, including Muslims.
From whatever has come in the media, it is clear that the Gujarat government affidavit (click HERE to read the report) is factually flawed for several reasons. First of all, while the Sachar Committee report title is “Social, Economic and Educational Status of Muslim Community in India”, it analyses the condition of Muslims vis-à-vis not just the Hindus, Other Backward Classes (OBCs), Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs) but also vis-à-vis other minority religious groups such as Christians, Sikhs, Buddhists and Parsis. In fact, even a cursory glance of the report suggests that its analysis is based on the condition of Muslims vis-à-vis STs/SCs, Other Hindus and “Others”, who include the non-Muslim religious minority groups.
In fact, the Sachar Committee compares each of the four categories – SC/ST, Other Hindus, Muslims and Others – even as banking heavily on available data on poverty, education, health, employment, access to credit, access to physical infrastructure, and so on. At certain places, it provides data for individual religious groups also, especially Christians and Sikhs. Both the Sachar Committee report as well as more recent data, made available in the 66th round National Sample Survey (NSS) reports provide, enough data to suggest why Muslims as minorities are more vulnerable than other minority communities and require a special treatment.
Take, for instance, incidence of poverty. In the Sachar Committee report, urban poverty, calculated on the basis of the NSS’ 61st round is found to be 38.4 per cent among Muslims, as against 36.4 per cent among SCs/STs, 25.1 per cent among OBCs, 8.3 per cent among general category Muslims, and a mere 12.2 per cent among religious minorities other than Muslims. As for rural poverty, the trend is found to be almost similar: it is 26.9 per cent among Muslims, as against 34.8 per cent among SCs/STs, 19.5 per cent among OBCs, nine per cent among general category Hindus, and 14.3 per cent among minorities other than Muslims.
The trend is not very different for Gujarat, where urban poverty among Muslims is found to be 24 per cent, as against 17 per cent among SCs/STs, 18 per cent among OBCs, a mere three per cent among general category Hindus, and zero (0) among minorities other than Muslims. In the rural areas the situation is better for Muslims than in the urban areas with seven per cent poor, as against 24 per cent among SCs/STs, 14 per cent among OBCs, three per cent among general category Hindus, and six per cent among minorities other than Muslims.
Based on these data, the Sachar Committee report says, “Muslims face fairly high levels of poverty. Their conditions on the whole are only slightly better than those of SCs/STs. As compared to rural areas, Muslims face much higher relative deprivation in urban areas. Over time changes in poverty levels also show that the economic conditions of Muslims in urban areas have not improved as much as the other socio-economic communities.” It adds, “While there are variations in the conditions of Muslims across states, the situation of the community in urban seems to be particularly bad in relative terms in almost all states except Kerala, Assam, Tamil Nadu, Orissa, Himachal Pradesh and Punjab. Their relative situation in rural areas is somewhat better but here again in most states poverty levels among Muslims are higher than all socio-religious communities, except SCs and STs.”
The NSS’ 66th round reports, put out in 2012-13 (based on 2009-10 survey), throw more light on this. The Muslims’ average monthly per capita expenditure (MPCE), which experts consider the basis of suggesting purchasing power of a population group, is found to be Rs 833 in rural India and Rs 1,272 in urban India. As compared to that, the figure for Hindus (all) is found to be Rs 888 in rural India and Rs 1,797 in urban India. Among Christians it is Rs 1,296 and Rs 2,053, respectively, and among Sikhs it is Rs 1,498 and Rs 2,180 respectively. Muslims’ MPCE, in fact, is found to be lower than STs, SCs and OBCs both in rural and urban areas. In rural India, for STs, it is Rs 873, for SCs Rs 979, and for OBCs Rs 1,281. In urban India, it is Rs 1,797 for STs, 1,444 among SCs and Rs 1,979 among OBCs.
While separate data of ratio of poverty among religious groups are not available in any of the NSS reports, social indicators suggest that Muslims are generally in the category of backward sections, including STs and SCs, of Hindu population. However, a recent study, by Dr Tanweer Fazal (“Millennium Development Goals and Muslims of India”, Oxfam India, 2013) has said that between 2004-05 and 2009-10, in urban areas, “poverty decline has been the slowest among Muslims (3.1 per cent per annum).” It adds, “In the rural areas, 26.2 per cent of all Muslims fall in the poorest quintile, whereas 25.6 of the non-Muslim OBCs and 34.2 of the SCs/STs fall in the same bracket of consumption expenditure”. As for Christians and Sikhs, the NSS has found that they are in a better position than both Hindus and Muslims.
The NSS report “Employment and Unemployment Situation among Major Religious Groups in India”, released in June 2013, provides data for the current attendance rates in educational institutions, i.e. the number of persons attending any educational institution per 1000 persons, which it says gives an idea of the “quality of human capital for the future workforce”. In the age-group 5-14, the attendance rate among rural Muslim males was 84.0 per cent, as against 87.5 per cent among Hindus (all), 94.9 per cent among Christians and 92.7 per cent among Sikhs. Among rural Muslim females, the attendance rate was found to be 77 per cent, as against 85.1 per cent Hindus (all), 94.1 per cent among Christians and 84.6 per cent among Sikhs.
As for the urban areas, the trend in attendance rate in the educational institutions in this age group is not found to be very different. Among males, it is 86.0 per cent among Muslims, as against Hindus’ 92.2 per cent, Christians’ 96.0 per cent, and Sikhs’ 92.2 per cent. As for females, it is 85.3 per cent among Muslims, as against 92.2 per cent among Hindus, 95.9 per cent among Christians and 84.5 per cent among Sikhs. Referring to yet another category – level of education among workers – the NSS suggests that Muslims are worse off than other religious groups. It says, “Among urban males, proportion of workers with level of education secondary and above was 58 per cent each for Christians and Sikhs whereas those were 56 per cent and 30 per cent, respectively, for Hindus and Muslims.”
An earlier analysis had pointed towards the fact that, in Gujarat, things are worse for Muslims. Quoting NSS report, it says, “The report finds 81.4 per cent attendance rate of Hindu children of the age group 5-14 in Gujarat’s educational institutes. This is against 78.7 per cent rate of attendance in the same age group among Muslims. What is more distressing is that the attendance rate of Muslim children in Gujarat is found to be one of the worst in India – with only three states performing poorer that Gujarat – Bihar (74.6 per cent), Rajasthan (73.2 per cent) and Uttar Pradesh (73.2 per cent). The report reveals that the all-India average of Muslim attendance rate in educational institutes in this age group is 82.3 per cent, higher by nearly four percentage points.”
From whatever has come in the media, it is clear that the Gujarat government affidavit (click HERE to read the report) is factually flawed for several reasons. First of all, while the Sachar Committee report title is “Social, Economic and Educational Status of Muslim Community in India”, it analyses the condition of Muslims vis-à-vis not just the Hindus, Other Backward Classes (OBCs), Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs) but also vis-à-vis other minority religious groups such as Christians, Sikhs, Buddhists and Parsis. In fact, even a cursory glance of the report suggests that its analysis is based on the condition of Muslims vis-à-vis STs/SCs, Other Hindus and “Others”, who include the non-Muslim religious minority groups.
In fact, the Sachar Committee compares each of the four categories – SC/ST, Other Hindus, Muslims and Others – even as banking heavily on available data on poverty, education, health, employment, access to credit, access to physical infrastructure, and so on. At certain places, it provides data for individual religious groups also, especially Christians and Sikhs. Both the Sachar Committee report as well as more recent data, made available in the 66th round National Sample Survey (NSS) reports provide, enough data to suggest why Muslims as minorities are more vulnerable than other minority communities and require a special treatment.
Take, for instance, incidence of poverty. In the Sachar Committee report, urban poverty, calculated on the basis of the NSS’ 61st round is found to be 38.4 per cent among Muslims, as against 36.4 per cent among SCs/STs, 25.1 per cent among OBCs, 8.3 per cent among general category Muslims, and a mere 12.2 per cent among religious minorities other than Muslims. As for rural poverty, the trend is found to be almost similar: it is 26.9 per cent among Muslims, as against 34.8 per cent among SCs/STs, 19.5 per cent among OBCs, nine per cent among general category Hindus, and 14.3 per cent among minorities other than Muslims.
The trend is not very different for Gujarat, where urban poverty among Muslims is found to be 24 per cent, as against 17 per cent among SCs/STs, 18 per cent among OBCs, a mere three per cent among general category Hindus, and zero (0) among minorities other than Muslims. In the rural areas the situation is better for Muslims than in the urban areas with seven per cent poor, as against 24 per cent among SCs/STs, 14 per cent among OBCs, three per cent among general category Hindus, and six per cent among minorities other than Muslims.
Based on these data, the Sachar Committee report says, “Muslims face fairly high levels of poverty. Their conditions on the whole are only slightly better than those of SCs/STs. As compared to rural areas, Muslims face much higher relative deprivation in urban areas. Over time changes in poverty levels also show that the economic conditions of Muslims in urban areas have not improved as much as the other socio-economic communities.” It adds, “While there are variations in the conditions of Muslims across states, the situation of the community in urban seems to be particularly bad in relative terms in almost all states except Kerala, Assam, Tamil Nadu, Orissa, Himachal Pradesh and Punjab. Their relative situation in rural areas is somewhat better but here again in most states poverty levels among Muslims are higher than all socio-religious communities, except SCs and STs.”
The NSS’ 66th round reports, put out in 2012-13 (based on 2009-10 survey), throw more light on this. The Muslims’ average monthly per capita expenditure (MPCE), which experts consider the basis of suggesting purchasing power of a population group, is found to be Rs 833 in rural India and Rs 1,272 in urban India. As compared to that, the figure for Hindus (all) is found to be Rs 888 in rural India and Rs 1,797 in urban India. Among Christians it is Rs 1,296 and Rs 2,053, respectively, and among Sikhs it is Rs 1,498 and Rs 2,180 respectively. Muslims’ MPCE, in fact, is found to be lower than STs, SCs and OBCs both in rural and urban areas. In rural India, for STs, it is Rs 873, for SCs Rs 979, and for OBCs Rs 1,281. In urban India, it is Rs 1,797 for STs, 1,444 among SCs and Rs 1,979 among OBCs.
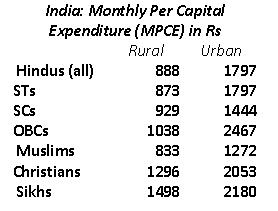 |
While separate data of ratio of poverty among religious groups are not available in any of the NSS reports, social indicators suggest that Muslims are generally in the category of backward sections, including STs and SCs, of Hindu population. However, a recent study, by Dr Tanweer Fazal (“Millennium Development Goals and Muslims of India”, Oxfam India, 2013) has said that between 2004-05 and 2009-10, in urban areas, “poverty decline has been the slowest among Muslims (3.1 per cent per annum).” It adds, “In the rural areas, 26.2 per cent of all Muslims fall in the poorest quintile, whereas 25.6 of the non-Muslim OBCs and 34.2 of the SCs/STs fall in the same bracket of consumption expenditure”. As for Christians and Sikhs, the NSS has found that they are in a better position than both Hindus and Muslims.
 |
As for the urban areas, the trend in attendance rate in the educational institutions in this age group is not found to be very different. Among males, it is 86.0 per cent among Muslims, as against Hindus’ 92.2 per cent, Christians’ 96.0 per cent, and Sikhs’ 92.2 per cent. As for females, it is 85.3 per cent among Muslims, as against 92.2 per cent among Hindus, 95.9 per cent among Christians and 84.5 per cent among Sikhs. Referring to yet another category – level of education among workers – the NSS suggests that Muslims are worse off than other religious groups. It says, “Among urban males, proportion of workers with level of education secondary and above was 58 per cent each for Christians and Sikhs whereas those were 56 per cent and 30 per cent, respectively, for Hindus and Muslims.”
 |
An earlier analysis had pointed towards the fact that, in Gujarat, things are worse for Muslims. Quoting NSS report, it says, “The report finds 81.4 per cent attendance rate of Hindu children of the age group 5-14 in Gujarat’s educational institutes. This is against 78.7 per cent rate of attendance in the same age group among Muslims. What is more distressing is that the attendance rate of Muslim children in Gujarat is found to be one of the worst in India – with only three states performing poorer that Gujarat – Bihar (74.6 per cent), Rajasthan (73.2 per cent) and Uttar Pradesh (73.2 per cent). The report reveals that the all-India average of Muslim attendance rate in educational institutes in this age group is 82.3 per cent, higher by nearly four percentage points.”

Comments