 |
| Sabarmati's Stagnant water body |
The Sabarmati river is one of the major west-flowing rivers in India. It originates in the Aravalli Range of the Udaipur district of Rajasthan and meets the Gulf of Khambhat of Arabian Sea after travelling 371 km in a south-westerly direction across Rajasthan and Gujarat. Forty eight km of the river length is in Rajasthan, while 323 km is in Gujarat. The Sabarmati is a seasonal river whose flows are dominated by the monsoon, with little or no flow post monsoon.
Recent articles in Counterview by Rohit Prajapati and Krishnakant of the Paryavaran Suraksha Samiti (PSS), describing the pollution of the Sabarmati River, follow years and years of neglect and a refusal to face up to the crucial health problem of the river.
Some years ago, this pollution was dramatically illustrated following work on the downstream dam, when the release of the water, revealed an incredible mass of rubbish, lining the sand on the river bed.
The extreme and totally unacceptable pollution is clearly identified and outlines the issues that must be faced.
Obviously, the idea of an edge-to-edge "lake-like" but basically stagnant water body is in complete contradiction with the climate and the cultural habits of the inhabitants of a city of now more than seven million, be it in India with its extreme climate conditions, or for that matter, anywhere else.
The original 1960s proposal of large platforms, stepping down, to a small but variable height and width water body, as opposed to the now constructed walls, would have made, had it been adopted, the discarding of refuse, sewage, industrial wastes and other effluents directly into the river totally impossible.
We must totally rethink the Ahmedabad Sabarmati river stretch in terms of its place within a project for the entire river basin as an ecological valley, from its source to the sea, and as an agricultural and environmental entity.
 |
| Prof Bernard Kohn |
Issues must be faced before a major health situation, as outlined by the Paryavaran Suraksha Samiti develops, with heavily polluted water discharged downstream that make the living conditions of the villagers, and the growing of healthy crops impossible.
1963-1967: My original Sabarmati river proposal
Together with colleagues of the Citizens’ Town Planning Group, I had suggested that the development on both sides of the 11 kilometers Ahmedabad stretch of the river, should be a part of a far larger Sabarmati river valley proposal.The project outlined the raising of then planned Vasna dam, just enough, to be able to control the desired height of the water all year long, and especially in the dry months, while respecting, the rest of the year, the other activities that used the sandy portions of the riverbed: the markets, the sand extraction, the ritual celebrations, the agricultural produce, as well as the festive occasional circus.
The public could access the river bed by a series of wide ghat-like steps coming down by a succeeding series of level-like platforms, and onwards to the water level. On both sides, without riverside thru traffic, a limited number of strictly defined access points perpendicular to the river were outlined, coming from the existing longitudinal roads, like Ashram road.
The proposal was shown to Morarji Desai, who was Chief Minister of the then Bombay State, and received the approval of the government. Hydraulic studies validated its feasibility, and as a result the dam was raised just enough to allow a possible and controllable water level.
From 1969 to 1999, everybody kept talking about the project but only the strict minimum construction necessary to channel wastewater directly into the river was undertaken.
Two programmatic drawings of the 1990 series of 12 sketches by me illustrated a step by step methodology of “thinking-machine”, as practiced by Patrick Geddes:
2000 onwards: Evolution of the project
In 2000, Bimal Patel, the well-known architect, committed himself and his large staff in promoting the project.He profoundly modified the “meaning” of the original proposal, from of a social and cultural project, to a design, more oriented to facilitating economic development, and guided by an impossible design idea of creating a yearlong edge to edge lake, “like Paris”, forgetting that in this example, the Seine, it is a flowing river.
The platforms, which had been initially projected coming down to the river became one single flat level with on both sides of the river of the 11 kilometers, eight meters high retaining walls, with large highways occupying the two banks.
True, the nature of the project has strong design qualities, but it serves a mistaken and abstract architectural presupposition.
I followed the evolution of the project, trying hard to reawaken public interest in the original social and environmental objectives, and away from the predominantly economic ones, while also attempting to counter the uninterrupted large proposed “ boulevards”, which in reality are highways.
In fact, these contribute to completely cut off easy citizens’ access and use of the river. They are obviously difficult to cross (as is the case today with the Ashram Road), and very difficult for a couple with small children and older citizens.
Bimal Patel's idea of creating a yearlong edge to edge lake like Paris forgets that Seine is a flowing river
To favour the fluidity and easy accessibility between the inhabitants of the densely woven neighborhoods of the city and the river, these highways, which are built basically for the serving of anticipated future real estate development, must be severely questioned.
This workshop was deeply indebted to Patrick Geddes, the extraordinary multidisciplinary thinker and doer who had visited and Ahmedabad in the 1920, and had written a noteworthy report which included a plea to not destroy the wall surrounding the old city.
An underlying objective of the workshop was to interest citizens, elected officials and university students to the overall concept of “a river for all”.
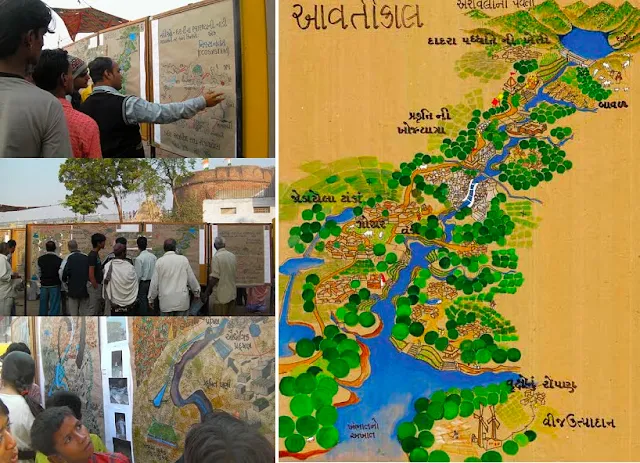
The 2008 and 2009 workshops concluded marvelous public exhibitions in the then still existing Sunday market in which participated different sections of the CEPT University: landscaping, city planning, architecture. Divided into eight teams the students surveyed different parts of the river, from the Aravalli Range, down to the Gulf of Khambhat.
This was one of the first times that an educational project, instead of staying in its cocoon, occupied a large public space and became involved with the daily life a large public. Significant articles (click here for one of them) calling for the creation of a Sabarmati ecological valley were published in many newspapers. Public conferences and exhibitions accompanied these endeavors.
However, in the following years, these positive initiatives were not followed up.The CEPT varsity interactive 2008-09 workshop
With both an educational and political goal, myself and CEPT colleagues organized a multidisciplinary workshop “Ecological Potential for the 400 kilometers of the Sabarmati river basin: A river for all”.This workshop was deeply indebted to Patrick Geddes, the extraordinary multidisciplinary thinker and doer who had visited and Ahmedabad in the 1920, and had written a noteworthy report which included a plea to not destroy the wall surrounding the old city.
An underlying objective of the workshop was to interest citizens, elected officials and university students to the overall concept of “a river for all”.
The 2008 and 2009 workshops concluded marvelous public exhibitions in the then still existing Sunday market in which participated different sections of the CEPT University: landscaping, city planning, architecture. Divided into eight teams the students surveyed different parts of the river, from the Aravalli Range, down to the Gulf of Khambhat.
This was one of the first times that an educational project, instead of staying in its cocoon, occupied a large public space and became involved with the daily life a large public. Significant articles (click here for one of them) calling for the creation of a Sabarmati ecological valley were published in many newspapers. Public conferences and exhibitions accompanied these endeavors.
Photographs below: The Sunday Market exhibition (left) in order to illustrate the impact and awakened interest that can be achieved with non-glossy illustrations. The drawing (right) illustrates the objectives of the benefits of treating the entire Sabarmati valley as one ecological entity.
We have no choice but to accept the fact that the concept of a stagnant lake is an aberration and a total mistake. We can immediately, we can immediately and significantly lower the water level. This will allow the water to flow and partly irrigate the potentially rich agricultural 200 kilometers of land beyond the city, down to the Gulf of Khambhat.
Our only option today is to: Open the gates and empty out a great part of the polluted water! At the same time, if along the 400 km, say some 100 metres wide tree plant is carried out, progressively, slowly, year by year, it would be a unifying inter social and cultural feat, as opposed to all the terrible separatist fundamentalist politics that are now ruining India.
---
*French-American architect, educator and urban planner (born 1931), currently at Le Puech, France; a founding member (along with BV Doshi and RN Vakil) of the School of Architecture, which is now one of the five faculties of CEPT University, Ahmedabad; credited with visualizing the Sabarmati Riverfront Development Project for the first time in the 1960s. Website: bernardkohn.org
Spring 2021: What can be the next steps
We can again in 2021 hold large democratic information forums and exhibitions, with in mind a city-wide referendum on different options that may be evaluated and discussed.We have no choice but to accept the fact that the concept of a stagnant lake is an aberration and a total mistake. We can immediately, we can immediately and significantly lower the water level. This will allow the water to flow and partly irrigate the potentially rich agricultural 200 kilometers of land beyond the city, down to the Gulf of Khambhat.
Our only option today is to: Open the gates and empty out a great part of the polluted water! At the same time, if along the 400 km, say some 100 metres wide tree plant is carried out, progressively, slowly, year by year, it would be a unifying inter social and cultural feat, as opposed to all the terrible separatist fundamentalist politics that are now ruining India.
---
*French-American architect, educator and urban planner (born 1931), currently at Le Puech, France; a founding member (along with BV Doshi and RN Vakil) of the School of Architecture, which is now one of the five faculties of CEPT University, Ahmedabad; credited with visualizing the Sabarmati Riverfront Development Project for the first time in the 1960s. Website: bernardkohn.org



Comments