India's investment in renewable energy down by 24%, Modi's target of 175GW by 2022 looks difficult: UN report
By A Representative
A United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) report has regretted that India’s investment chart in renewable energy has been “oscillating in the $6-14 billion range since 2010 – still not reaching the sort of levels that would be required for that country to meet Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s ambitious goals for 2022” -- 175 gigawatts (GW).
Prepared jointly by UNEP’s Economy Division, Frankfurt School-UNEP Collaborating Centre for Climate and Sustainable Energy Finance, and Bloomberg New Energy Finance, the report, “Global Trends in Renewable Energy Investment 2018”, says, this has happened even as China’s global investment in renewables, excluding large hydro last year, “alone representing 45%, up from 35% in 2016.”
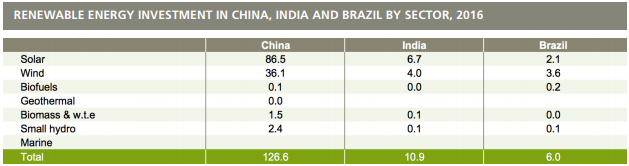
Supported by Germany’s Federal Ministry of Environment, Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety, the report says that China’s $126.6 billion investment is characterized by the dominance of solar, at $86.5 billion (up 58% year-on-year and the highest ever), far ahead of wind at $36.1 billion (down 6%), small hydro down 7% at $2.4 billion and biomass and waste-to-energy also down 7% at $1.5 billion.”
Praising China, the report states, “The spectacular build-out of 53GW of solar took place despite worries over a growing subsidy burden and worsening power curtailment. China’s regulators, under pressure from the industry, were slow to curb build of utility-scale projects outside allocated government quotas.”
While “India came fourth in the world rankings by country for renewable energy investment last year”, the report laments, at $10.9 billion, this was “down 20%.” Sectorwise, the report says, in India, “solar took the biggest share, at $6.7 billion, with wind at $4 billion”, adding, “These lead sectors were up 3%, and down 41%, in dollar terms respectively.”
A United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) report has regretted that India’s investment chart in renewable energy has been “oscillating in the $6-14 billion range since 2010 – still not reaching the sort of levels that would be required for that country to meet Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s ambitious goals for 2022” -- 175 gigawatts (GW).
Prepared jointly by UNEP’s Economy Division, Frankfurt School-UNEP Collaborating Centre for Climate and Sustainable Energy Finance, and Bloomberg New Energy Finance, the report, “Global Trends in Renewable Energy Investment 2018”, says, this has happened even as China’s global investment in renewables, excluding large hydro last year, “alone representing 45%, up from 35% in 2016.”
Supported by Germany’s Federal Ministry of Environment, Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety, the report says that China’s $126.6 billion investment is characterized by the dominance of solar, at $86.5 billion (up 58% year-on-year and the highest ever), far ahead of wind at $36.1 billion (down 6%), small hydro down 7% at $2.4 billion and biomass and waste-to-energy also down 7% at $1.5 billion.”
Praising China, the report states, “The spectacular build-out of 53GW of solar took place despite worries over a growing subsidy burden and worsening power curtailment. China’s regulators, under pressure from the industry, were slow to curb build of utility-scale projects outside allocated government quotas.”
While “India came fourth in the world rankings by country for renewable energy investment last year”, the report laments, at $10.9 billion, this was “down 20%.” Sectorwise, the report says, in India, “solar took the biggest share, at $6.7 billion, with wind at $4 billion”, adding, “These lead sectors were up 3%, and down 41%, in dollar terms respectively.”
According to the report, in India, “solar activity was held back by an unexpected rise in photovoltaic (PV) module prices in local currency terms, due to a sudden reduction in the oversupply of imported Chinese units, exacerbated by the imposition of a 7.5% import duty on modules, and a local goods and service tax on panels. There was also a slowing in the pace of solar auctions around India.”
While hoping that “in the medium term, PV installations” may increase sharply, “as India seeks to hit its ambitious target of 100GW of solar by 2022”, the report notes, “However, that acceleration did not materialize in 2017, even though “there were, nevertheless, several projects financed that rivalled in size anything financed in China last year – including the APPGCL Andhra Pradesh PV park, at 500MW and an estimated $400 million.”
Providing a list of 10 top investors in renewable energy, the report, however, does not fail to note, “India saw lukewarm demand for new project finance in 2017, with investment falling 24% to $9.4 billion.”
By contrast, “China’s first place position is cemented at $103.3 billion, a 14% increase on the previous year.” In 2017, it adds, “the US was down 1%, Germany with $7.6 billion, down 32%, and the UK with $6.7 billion, down 67%. New entrants to the top 10 list are Australia, Mexico, Brazil and Sweden in order of investment value.”
Pointing out that investment in small-scale solar projects of less than 1MW capacity may have “increased”, the report says, in India, as in France and Belgium, this “has been driven chiefly by government policy, mainly in the form of financial subsidies.”
Noting a silver lining, the report says, while internationally “venture capital and private equity (VC/PE) investment in renewable energy fell by exactly a third in 2017 to $1.8 billion, just a sixth of its 2008 peak of more than $10 billion… India was a bright spot, gaining 27% to $457 million.”
“India’s VC/PE investment grew strongly because it secured three of the five largest deals. Two of those were wind companies raising funds to expand in that country, a fiercely competitive market with huge growth potential that is attracting many foreign investors”, the report says.
While hoping that “in the medium term, PV installations” may increase sharply, “as India seeks to hit its ambitious target of 100GW of solar by 2022”, the report notes, “However, that acceleration did not materialize in 2017, even though “there were, nevertheless, several projects financed that rivalled in size anything financed in China last year – including the APPGCL Andhra Pradesh PV park, at 500MW and an estimated $400 million.”
Providing a list of 10 top investors in renewable energy, the report, however, does not fail to note, “India saw lukewarm demand for new project finance in 2017, with investment falling 24% to $9.4 billion.”
By contrast, “China’s first place position is cemented at $103.3 billion, a 14% increase on the previous year.” In 2017, it adds, “the US was down 1%, Germany with $7.6 billion, down 32%, and the UK with $6.7 billion, down 67%. New entrants to the top 10 list are Australia, Mexico, Brazil and Sweden in order of investment value.”
Pointing out that investment in small-scale solar projects of less than 1MW capacity may have “increased”, the report says, in India, as in France and Belgium, this “has been driven chiefly by government policy, mainly in the form of financial subsidies.”
Noting a silver lining, the report says, while internationally “venture capital and private equity (VC/PE) investment in renewable energy fell by exactly a third in 2017 to $1.8 billion, just a sixth of its 2008 peak of more than $10 billion… India was a bright spot, gaining 27% to $457 million.”
“India’s VC/PE investment grew strongly because it secured three of the five largest deals. Two of those were wind companies raising funds to expand in that country, a fiercely competitive market with huge growth potential that is attracting many foreign investors”, the report says.


Comments