By Jag Jivan
The Reserve Bank of India’s annual report on the state of state finances has been released. Providing inter-state comparison on a large number of indicators, the report suggests that Gujarat continues to spend less on the social sector, despite state government claims. A counterview.org analysis:
The latest Reserve Bank of India (RBI) report, “State Finances: A Study of Budgets of 2013-14”, has once again demonstrated that the Gujarat government has not been spending enough on social sector, despite its poor human development indicators. Brought out in January 2014, the report – an annual exercise – says that in India as a whole “the expenditure pattern revealed an improvement in quality, as reflected in sharp increases in development expenditure, particularly social sector expenditure.”
However, the data the RBI report has put out go to show that Gujarat has failed to improve upon its social sector expenditure in the recent past. In fact, if the report is any indicator, overall spending on the social sector – which includes not just education and health but also expenditure on rural development, food storage and warehousing – has stagnated over the last four years.
Thus, the Gujarat government’s social sector expenditure in 2010-11 was 39.9 per cent of the aggregate budgetary disbursement, which came down to 38.2 per cent in 2011-12, increased to 39.0 per cent in 2012-13, and is projected to be 39.1 per cent in 2013-14.
Worse, Gujarat’s projected social sector expenditure as percent of budgetary disbursement in 2013-14, says the RBI report, is less than several states, including Andhra Pradesh (41.8 per cent), Bihar (45 per cent), Chhattisgarh (53.6 per cent), Haryana (42.1 per cent), Madhya Pradesh (41.6 per cent), Jharkhand (43.9 per cent), Maharashtra (43.2 per cent), Odisha (39.9 per cent), Rajasthan (43.3 per cent), Uttar Pradesh (39.6 per cent), and West Bengal (43 per cent).
What is particularly disconcerting about disbursement of budgetary allocation for the social sector is that it has failed to rise over the years as percentage of the Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP). Social sector expenditure as per cent of GSDP is calculated in order to find out how much does the government support the social sector even as the economy is expanding.
Thus, Gujarat’s projected social sector expenditure for the year 2013-14 as per cent of GSDP at 5.5 per cent is lower than all major 17 states, which the RBI report has separated for analytical considerations, except one – Maharashtra (5.4 per cent). The projected national average spending for the social sector for all states is 6.6 per cent, the report suggests.
A comparison between two set of four-years — 2008-10 and 2010-13 — suggests that there has been virtually no change in allocation of funds – in 2008-10, it was 5.2 per cent of the GSDP, and in 2010-13 it was 5.3 per cent of the GSDP. On the other hand, the national average on this count was six per cent in 2008-10 and 6.1 per cent in 2010-13.
The RBI’s report is based on the data provided by respective state governments. Says the report, “This report is based on the receipts and expenditure data presented in the budget documents of 28 state governments. Data in respect of two Union Territories (UTs) with legislature, viz., National Capital Territory of Delhi (NCT Delhi) and Puducherry are provided separately as memo item in all statements. The analysis conforms to the data presented in state budgets and the accounting classification thereof.”
The RBI report notes with satisfaction about the country as a whole, that “important sectors such as agriculture, education, medical and public health, and infrastructure development have been accorded priority in state budgets”, adding, this suggests “continuation of policy initiatives to improve transparency, governance and delivery of various public services in 2013-14.”
But is not true for Gujarat, and the report finds things are particularly bad for education. Thus, the projected expenditure for education in Gujarat as per cent of the total budgetary disbursement in 2013-14 was 13.9 per cent, down from 15.9 per cent in 2010-11, 15.8 per cent in 2011-12, and 13.2 per cent in 2012-13. Gujarat projected education expenditure in 2013-14 as per cent of total budgetary disbursement was found to be lower than all states except Andhra Pradesh (13.5 per cent) and Punjab (13.4 per cent). The national average for 2013-14 is 16.5 per cent.
The only consolation for the Gujarat government in social sector spending is the health sector, in which it spent 4.9 per cent of the total budget in 2013-14, which is higher than most states except Goa (5.3 per cent), Kerala (5.2 per cent), Punjab (5.1 per cent), Rajasthan (5.3 per cent), and Uttar Pradesh (5.1 per cent).
In this sector, which includes medical and public health and family welfare, sports and art and culture, the national average for 2013-14 was found to be 4.5 per cent – lower than Gujarat’s. The rise in the expenditure as per cent of budgetary allocation in Gujarat was also consistent – it was 4.2 per cent in 2010-11 and 2011-12, and reached 4.7 per cent in 2012-13.
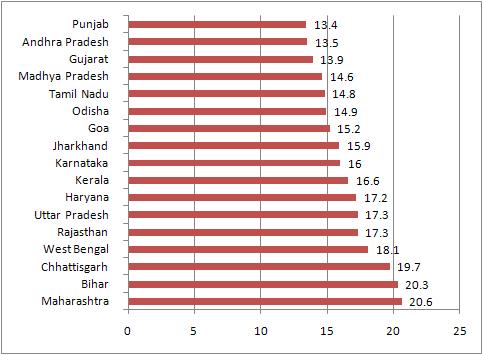 |
| Projected expenditure on education 2013-14 (% budgetary allocation) |
Thus, the Gujarat government’s social sector expenditure in 2010-11 was 39.9 per cent of the aggregate budgetary disbursement, which came down to 38.2 per cent in 2011-12, increased to 39.0 per cent in 2012-13, and is projected to be 39.1 per cent in 2013-14.
Worse, Gujarat’s projected social sector expenditure as percent of budgetary disbursement in 2013-14, says the RBI report, is less than several states, including Andhra Pradesh (41.8 per cent), Bihar (45 per cent), Chhattisgarh (53.6 per cent), Haryana (42.1 per cent), Madhya Pradesh (41.6 per cent), Jharkhand (43.9 per cent), Maharashtra (43.2 per cent), Odisha (39.9 per cent), Rajasthan (43.3 per cent), Uttar Pradesh (39.6 per cent), and West Bengal (43 per cent).
What is particularly disconcerting about disbursement of budgetary allocation for the social sector is that it has failed to rise over the years as percentage of the Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP). Social sector expenditure as per cent of GSDP is calculated in order to find out how much does the government support the social sector even as the economy is expanding.
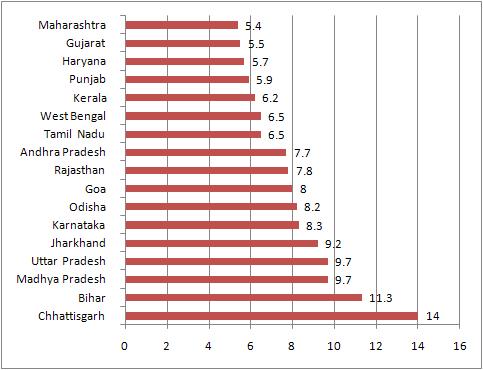 |
| Projected social sector expenditure: % of GSDP 2013-14 |
Thus, Gujarat’s projected social sector expenditure for the year 2013-14 as per cent of GSDP at 5.5 per cent is lower than all major 17 states, which the RBI report has separated for analytical considerations, except one – Maharashtra (5.4 per cent). The projected national average spending for the social sector for all states is 6.6 per cent, the report suggests.
A comparison between two set of four-years — 2008-10 and 2010-13 — suggests that there has been virtually no change in allocation of funds – in 2008-10, it was 5.2 per cent of the GSDP, and in 2010-13 it was 5.3 per cent of the GSDP. On the other hand, the national average on this count was six per cent in 2008-10 and 6.1 per cent in 2010-13.
The RBI’s report is based on the data provided by respective state governments. Says the report, “This report is based on the receipts and expenditure data presented in the budget documents of 28 state governments. Data in respect of two Union Territories (UTs) with legislature, viz., National Capital Territory of Delhi (NCT Delhi) and Puducherry are provided separately as memo item in all statements. The analysis conforms to the data presented in state budgets and the accounting classification thereof.”
The RBI report notes with satisfaction about the country as a whole, that “important sectors such as agriculture, education, medical and public health, and infrastructure development have been accorded priority in state budgets”, adding, this suggests “continuation of policy initiatives to improve transparency, governance and delivery of various public services in 2013-14.”
But is not true for Gujarat, and the report finds things are particularly bad for education. Thus, the projected expenditure for education in Gujarat as per cent of the total budgetary disbursement in 2013-14 was 13.9 per cent, down from 15.9 per cent in 2010-11, 15.8 per cent in 2011-12, and 13.2 per cent in 2012-13. Gujarat projected education expenditure in 2013-14 as per cent of total budgetary disbursement was found to be lower than all states except Andhra Pradesh (13.5 per cent) and Punjab (13.4 per cent). The national average for 2013-14 is 16.5 per cent.
The only consolation for the Gujarat government in social sector spending is the health sector, in which it spent 4.9 per cent of the total budget in 2013-14, which is higher than most states except Goa (5.3 per cent), Kerala (5.2 per cent), Punjab (5.1 per cent), Rajasthan (5.3 per cent), and Uttar Pradesh (5.1 per cent).
In this sector, which includes medical and public health and family welfare, sports and art and culture, the national average for 2013-14 was found to be 4.5 per cent – lower than Gujarat’s. The rise in the expenditure as per cent of budgetary allocation in Gujarat was also consistent – it was 4.2 per cent in 2010-11 and 2011-12, and reached 4.7 per cent in 2012-13.


Comments