By Prof RR Prasad*
In the 2023–24 Union Budget, which was released on February 1, 2023, Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced a mission for the welfare of Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs). For the following three years, a budget of Rs 15,000 crore has been set out for the group's socioeconomic development. One of the seven Saptarishi goals outlined in this year's Budget, "Reaching The Last Mile," would include the start of the Pradhan Mantri PVTG Mission.
In the 2023–24 Union Budget, which was released on February 1, 2023, Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced a mission for the welfare of Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs). For the following three years, a budget of Rs 15,000 crore has been set out for the group's socioeconomic development. One of the seven Saptarishi goals outlined in this year's Budget, "Reaching The Last Mile," would include the start of the Pradhan Mantri PVTG Mission.
In India, there are 75 PVTGs that will profit from this programme. The PVTG development mission would provide secure homes, clean drinking water, education, nutrition, road and telecom connectivity, and livelihood to the tribal populations that are particularly vulnerable.
Characteristics of the PVTGs
The PVTGs) are the most underprivileged and deprived tribal communities in India. PVTGs are those scheduled tribes characterized by:- Pre-agriculture level of technology,
- Stagnant or declining population,
- Extremely low literacy, and 4.Subsistence level of economy.
The Government of India had started identification of PVTGs in 1975. As per 2001 census, there are 75 tribes identified as PVTGs with a total population of 32.6 lakh and residing in 17 states & 1 Union Territory. PVTGs live in remote and scattered geographical locations. More than 80% population of PVTGs is found in MP, Orissa, Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, Jharkhand, Tamil Nadu, Tripura and Chhattisgarh.
Earlier called primitive tribal groups - a misnomer as they lived intricately evolved highly ecological lifestyles in close relation to forested homesteads - they are now called particularly vulnerable tribal groups, as they became vulnerable to shrinking habitats and eroding traditional occupations which has threatened their survival.
Today, PVTGs living in interior pockets and inaccessible places, are becoming vulnerable to hunger/starvation, malnutrition and ill-health. Some of them are even on the verge of extinction. They include Shompens, Jarawas, Sentinelese of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands; Bondos of Orissa, Cholanaickans of Kerala, the Abujhmarias of Chhattisgarh; and Birhors of Jharkhand.
Most of these groups are small in number, have not attained any significant level of social and economic progress and generally inhabit remote localities having poor infrastructure and administrative support. Priorities are, therefore, required to be accorded for their protection and development, and checking the declining trend of their population.
It is therefore absolutely necessary that plans for development of the PVTGs and their protection be prepared on certain identifiable, verifiable and quantifiable criteria; particularly with respect to the nature, extent and degree of vulnerabilities from which they suffer. Once the nature of and extent of vulnerability is known, then it would be important to develop criteria for interventions to reduce vulnerability among the PVTGs.
Earlier called primitive tribal groups - a misnomer as they lived intricately evolved highly ecological lifestyles in close relation to forested homesteads - they are now called particularly vulnerable tribal groups, as they became vulnerable to shrinking habitats and eroding traditional occupations which has threatened their survival.
Today, PVTGs living in interior pockets and inaccessible places, are becoming vulnerable to hunger/starvation, malnutrition and ill-health. Some of them are even on the verge of extinction. They include Shompens, Jarawas, Sentinelese of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands; Bondos of Orissa, Cholanaickans of Kerala, the Abujhmarias of Chhattisgarh; and Birhors of Jharkhand.
Most of these groups are small in number, have not attained any significant level of social and economic progress and generally inhabit remote localities having poor infrastructure and administrative support. Priorities are, therefore, required to be accorded for their protection and development, and checking the declining trend of their population.
It is therefore absolutely necessary that plans for development of the PVTGs and their protection be prepared on certain identifiable, verifiable and quantifiable criteria; particularly with respect to the nature, extent and degree of vulnerabilities from which they suffer. Once the nature of and extent of vulnerability is known, then it would be important to develop criteria for interventions to reduce vulnerability among the PVTGs.
Reducing and vanishing vulnerability
Notions of vulnerability play an increasingly important role in shaping policies and interventions targeted at improving or intervening in the lives of those identified as ‘in need’. In times of economic austerity and limited welfare resources, ideas about ‘vulnerability’ and the prioritization of ‘vulnerable groups’ take on further significance in social policy.‘Vulnerability’ is rarely centre stage in policy, but bringing it to the fore in analysis of welfare provision reveals important assumptions and trends. On first consideration, the concept of ‘vulnerability’ seems to resonate strongly with the pursuit of social justice. Vulnerability is a term used to describe exposure to hazards and shocks. People are more vulnerable if they are more likely to be badly affected by events outside their control.
The ability to foresee, cope with, resist, and recover from the effects of a hazard is influenced by a person's or group's traits as well as their environment. It involves a combination of factors that determine the degree to which someone’s life, livelihood, property and other assets are put at risk by a discrete and identifiable event (or series or cascade of such events) in nature and society.
The VAM Unit, World Food Programme (2002) developed the conceptual framework for understanding vulnerability and explained that:
The ability to foresee, cope with, resist, and recover from the effects of a hazard is influenced by a person's or group's traits as well as their environment. It involves a combination of factors that determine the degree to which someone’s life, livelihood, property and other assets are put at risk by a discrete and identifiable event (or series or cascade of such events) in nature and society.
The VAM Unit, World Food Programme (2002) developed the conceptual framework for understanding vulnerability and explained that:
Vulnerability = Exposure to Hazards + Ability to Cope
In this framework, exposure to hazards is seen as a community-level issue experienced by all households, whereas coping ability varies from household to household. The determinants of coping capacity include levels of assets, income, and consumption, and the ability to diversify sources of income and consumption to mitigate the effects of the risk that households face, basic access to resources and infrastructure is an important determinant of coping capacity. The ability to diversify incomes and consumption depends largely on access to labour markets, markets for food, efficient credit markets, and access to community and public support (safety net) services.
Understanding households coping vulnerability is not a commonly accepted concept. The concept has interlinks with the notion of social exclusion, poverty, discrimination and marginalization. In fact, vulnerability is obscure as a stand-alone concept and only serves a practical purpose once we ask the question, vulnerability to what?
The tendency in answering this question is to isolate a single cause of vulnerability. However, new research findings help us in moving away from this approach to a more systemic perspective, in recognition of the complexity of vulnerability and the interaction of various causes and effects of vulnerability.
Indexing vulnerability
Vulnerability among the PVTGs may be examined from five dimensions namely,- economic,
- educational,
- demographic,
- spatial, and
- environmental.
In order to measure vulnerabilities of the PVTGs with respect to each of these dimensions, we need to identify verifiable and measurable indicators for each dimension.
After collection of primary data on each indicator of different dimensions, values may be assigned to each indicator and then compared with the actual values secured from field investigations. Subsequently vulnerability scores can be derived from the average scores. Similarly, for calculating the vulnerability index among the PVTGs, values may be assigned to each indicator between 1.00 to 0.1 and actual value calculated for the various indicators by adopting the below given formula:
By analyzing the vulnerability index in all the five dimensions and indicators, it would be possible to appreciate the relative severity of the factors that contribute towards vulnerability. It is also important to understand that higher the value of vulnerability index, the greater would be the case for making such interventions that contribute towards reduction of the vulnerabilities of the PVTG in all dimensions. In a research study conducted by the author among the 8 PVTGs of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana States, vulnerability index and ranks were assessed using the above formula (Table 1).
The normalization is given by:
By analyzing the vulnerability index in all the five dimensions and indicators, it would be possible to appreciate the relative severity of the factors that contribute towards vulnerability. It is also important to understand that higher the value of vulnerability index, the greater would be the case for making such interventions that contribute towards reduction of the vulnerabilities of the PVTG in all dimensions. In a research study conducted by the author among the 8 PVTGs of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana States, vulnerability index and ranks were assessed using the above formula (Table 1).
Vulnerability intervention index
In the light of the understanding of the various dimensions of vulnerabilities among the studied PVTGs, the author suggested essentially three areas of interventions. They are:- Interventions for bringing about economic transformation;
- Interventions for educational development; and
- Interventions in the demographic dimension to ensure increase in the population of the PVTGs.
The normalization is given by:
Vulnerability intervention score for economic transformation was highest among the Chenchu (74) PVTG while it was lowest for the Konda Reddy PVTG (43). Similarly, in the context of vulnerability score for the educational development of the PVTGs, it was highest (64) among the Chenchu PVTG and lowest (44) among the Gadaba PVTG.
Likewise, one can see that the vulnerability intervention score in the demographic domain was again highest among the Chenchu (64) and lowest among the Konda Reddy (41). Once can calculate the total vulnerability score with respect to all the three dimensions for all the eight studied PVTGs, it would be seen from the Table 2 that it is highest (205) among the Chenchu PVTG and lowest among the Konda Reddi (135).
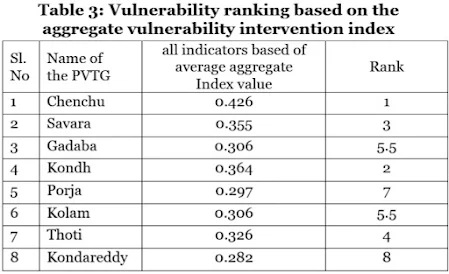
The total vulnerability intervention score with respect to all the three dimensions for all the eight studied PVTGs may be seen in Table 3 and it would be seen that it is highest (205) among the Chenchu PVTG and lowest among the Konda Reddi (135).
Vulnerability intervention score and the vulnerability intervention index are very good indicators of the nature and priority areas of interventions that are required to be undertaken with respect to different PVTGs in the different dimensions of their socio-economic living conditions.
The total vulnerability intervention score with respect to all the three dimensions for all the eight studied PVTGs may be seen in Table 3 and it would be seen that it is highest (205) among the Chenchu PVTG and lowest among the Konda Reddi (135).
Vulnerability intervention score and the vulnerability intervention index are very good indicators of the nature and priority areas of interventions that are required to be undertaken with respect to different PVTGs in the different dimensions of their socio-economic living conditions.
Summing up
In order to ensure transformation of the members of the PVTGs from a stage marked by pre-agricultural level of technology to a stage of settled cultivation, it is necessary that the policy planners take a solemn pledge to protect PVTGs’ livelihoods, cultural identity and habitats while facilitating their access to development programmes and services and to improve their quality of life.This pledge can be seen honoured only when we decide to make the following calibrated interventions in the various dimensions of the vulnerabilities which afflict the PVTGs:
*Was associated with the National Institute of Rural Development & Panchayati Raj (NIRDPR), Hyderabad
- Create enabling environment to respect, protect, and fulfill PVTGs' rights
- Formulate sustainable livelihood strategies for the PVTGs
- Participatory development approach be followed
- Evolve effective service delivery mechanism for the development of the PVTGs
- Separate Census for the PVTGs should be undertaken
- Control factors that contribute to decline in the population of the (PVTGs).
- Launch special drive to improve educational status of the PVTGs
- Monitoring of socio-economic transformation
- Use the Vulnerability Index and Vulnerability Intervention Index as the basis for funding Development of the PVTGs
- Vulnerability Index should be made the basis for delisting some of the PVTGs from the PVTG category/status
- Since spatial and environmental dimensions are crucial determinants of vulnerability, it is important that the tribes be declared as PVTG after taking into consideration the spatial and environmental dimensions of their habitat.
*Was associated with the National Institute of Rural Development & Panchayati Raj (NIRDPR), Hyderabad






Comments
Regards
NK Vaid