
By Birendra Ram Mishra, Ramprashan Singh, Santosh Kumar Pradhan, Sonu Khan, Gatha G Namboothiri*
Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakram (PMJVK), anchored by the Ministry of Minority Affairs, is the revamped and restructured version of the Multi-sectoral Development Programme (MsDP). A Centrally Sponsored Infrastructure Support Scheme, PMJVK aims to provide the minority communities with socio-economic infrastructure facilities in the field of education, health and skill development. It is one of the several schemes covered under the Prime Minister’s New 15-Point Programme for the Welfare of Minorities, launched in 2005.
It was launched in 90 Minority Concentrated Districts. However, since the size of the districts were too big, the benefits seldom reached the grassroots. Thus, in 2012-14, the focus was shifted to Minority Concentration Blocks (MCB), Minority Concentration Towns (MCT) and Clusters of Minority Concentration Villages (Cluster) to ensure that the grassroots level communities are directly targeted.
In the financial year 2019-20, the Ministry of Minority Affairs was allocated almost 4700.00 crores. Out of this, 31.28% was allocated for PMJVK, the second-highest allocation by the Ministry after ‘Education empowerment’.
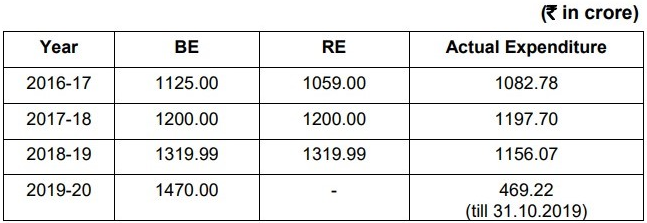
Budget Estimate, Revised Estimate and Actual expenditure incurred under the PMJVK: DEMANDS FOR GRANTS (2019-20) FOURTH REPORT: MINISTRY OF MINORITY AFFAIRS
During one of our visits to Sisi, a Muslim-dominated village where we work, in the Gumla district of Jharkhand, we observed that the village had not been declared as a Cluster under the Multi-sectoral Development Programme (MsDP) scheme. The same is true for other villages such as Kotam, Katri, Luto and Panso. Most of these villages do not have a Primary Health Center (‘PHC’). While there is a designated PHC in Kotam, it has ill-equipped infrastructure and a constant staff shortage. The primary school in Kotam is used by Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF) as a camp. Declaring these villages as minority clusters is one way to ensure that they get the much-needed attention from the government.
Earlier, the requirement to be covered by the MsDP scheme was for a District or a Block to have at least 50% minority population. In the revamped scheme now titled Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakram (PMJVK), the criterion was lowered to a substantial minority population of 25%. Further, clusters of contiguous villages with a minimum of 25% minority population but are not within the identified Minority Concentrated Blocks (‘MCB’) can now be declared as Clusters of Minority Concentration Villages (‘Clusters’). However, in reality, villages have not been declared either under MCB or as Clusters.
Even when declarations have happened under this scheme, they have been based on grossly inaccurate baseline surveys. Our experience in Gumla shows that a village that was shown to have 70-80% of the Christian population only had two or three Christian households. The minority population of another village was declared to be 112%, which is a mathematical impossibility.
In 2017, an intervention titled Rehnuma, anchored by National Foundation for India (‘NFI’) and Centre for Social Justice (‘CSJ’), released their study report spanning seven states. The report, which studied the implementation of the Prime Minister’s New 15-Point Programme for the Welfare of Minorities (launched in 2005), noted as follows about the MsDP;
“An important concern with respect to MsDP is the low levels of physical outcome progress indicating poor rate of work completion under the programme. Hence, as of now, even though around 80% of the proposed funds for MsDP under the 12th Five-Year Plan (‘FYP’) have been spent, there is poor progress on the ground. This suggests an urgent need for better implementation of the programme by the Ministry.”
The reality remains the same, as can be seen from the situation in Jharkhand. This problem is not unique to one or two states in the country. As of December 2019, the PMJVK scheme is yet to take off in 8 states as projects have not been approved in those states, while in a few other states, funds have been sanctioned, but not projects. There are also states like Uttar Pradesh, where the state government had only utilised 10% of the funds released under the Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakram (PMJVK) scheme 2019-2020.
The Parliamentary Standing Committee Report on Social Justice and Empowerment titled ‘Implementation of Scheme of Multi-Sectoral Development Programme/ Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakram’ of August 2018 noted several shortcomings of the scheme. The report noted that due to a lack of disaggregated data regarding the communities covered by the scheme, it was not possible to assess the impact of the scheme on the targeted communities. It noted with concern that the projects relating to drinking water supply and pucca housing had not been included in PMJVK. It also recommended the completion of education and health-related projects sanctioned/ undertaken. In addition, there were multiple issues such as the long gestation period of projects, delay in transfer of funds etc, which led to low utilisation of funds. The report also pointed out that; “the Committee found that despite having several monitoring mechanisms, the impact of MsDP is hardly visible in the Minority Concentration Areas”.
Since its inception, the scheme been plagued by inefficient processes and systems, leading to substantial implementational hurdles. This scheme is monitored and regulated by various committees formed at various administrative levels such as the State Level Committee, District Level Committee, Block Level Committees, etc. However, it has been observed that the members in the Committees formed do not receive requisite training. This causes problems as they remain unclear on how to carry out their functions exactly. The unclarity further makes it difficult for these Committees to determine where/which infrastructure is to be developed. A second main factor working against the efficacy of PMJVK is the lack of awareness about the scheme at the ground level. In such situations of state failure, civil society organisations and non-governmental organisations are left to fulfil the state’s obligations. They have to step forward now and exert pressure on the authorities to declare clusters and identify projects.
This dilution in criteria has also, however, raised a concern too. The Sachar committee report, which paved the way for many minority-targeted schemes, including MsDP, was instrumental in demonstrating that the Muslim community lagged behind most communities on socio-economic indices. While reducing the population percentage parameter has ensured that the geographical coverage is more for the scheme, one of the primary beneficiaries (Muslims) is once again left with lesser resources.
—
The authors are associated with the Jharkhand Unit of the Centre for Social Justiceand are actively involved in providing legal representation to marginalised communities in Gumla. They may be contacted at rehnuma.jharkhand@gmail.com. Views are personal. This article was initially published in Newsclick

During one of our visits to Sisi, a Muslim-dominated village where we work, in the Gumla district of Jharkhand, we observed that the village had not been declared as a Cluster under the Multi-sectoral Development Programme (MsDP) scheme. The same is true for other villages such as Kotam, Katri, Luto and Panso. Most of these villages do not have a Primary Health Center (‘PHC’). While there is a designated PHC in Kotam, it has ill-equipped infrastructure and a constant staff shortage. The primary school in Kotam is used by Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF) as a camp. Declaring these villages as minority clusters is one way to ensure that they get the much-needed attention from the government.
Earlier, the requirement to be covered by the MsDP scheme was for a District or a Block to have at least 50% minority population. In the revamped scheme now titled Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakram (PMJVK), the criterion was lowered to a substantial minority population of 25%. Further, clusters of contiguous villages with a minimum of 25% minority population but are not within the identified Minority Concentrated Blocks (‘MCB’) can now be declared as Clusters of Minority Concentration Villages (‘Clusters’). However, in reality, villages have not been declared either under MCB or as Clusters.
Even when declarations have happened under this scheme, they have been based on grossly inaccurate baseline surveys. Our experience in Gumla shows that a village that was shown to have 70-80% of the Christian population only had two or three Christian households. The minority population of another village was declared to be 112%, which is a mathematical impossibility.
In 2017, an intervention titled Rehnuma, anchored by National Foundation for India (‘NFI’) and Centre for Social Justice (‘CSJ’), released their study report spanning seven states. The report, which studied the implementation of the Prime Minister’s New 15-Point Programme for the Welfare of Minorities (launched in 2005), noted as follows about the MsDP;
“An important concern with respect to MsDP is the low levels of physical outcome progress indicating poor rate of work completion under the programme. Hence, as of now, even though around 80% of the proposed funds for MsDP under the 12th Five-Year Plan (‘FYP’) have been spent, there is poor progress on the ground. This suggests an urgent need for better implementation of the programme by the Ministry.”
The reality remains the same, as can be seen from the situation in Jharkhand. This problem is not unique to one or two states in the country. As of December 2019, the PMJVK scheme is yet to take off in 8 states as projects have not been approved in those states, while in a few other states, funds have been sanctioned, but not projects. There are also states like Uttar Pradesh, where the state government had only utilised 10% of the funds released under the Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakram (PMJVK) scheme 2019-2020.
The Parliamentary Standing Committee Report on Social Justice and Empowerment titled ‘Implementation of Scheme of Multi-Sectoral Development Programme/ Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakram’ of August 2018 noted several shortcomings of the scheme. The report noted that due to a lack of disaggregated data regarding the communities covered by the scheme, it was not possible to assess the impact of the scheme on the targeted communities. It noted with concern that the projects relating to drinking water supply and pucca housing had not been included in PMJVK. It also recommended the completion of education and health-related projects sanctioned/ undertaken. In addition, there were multiple issues such as the long gestation period of projects, delay in transfer of funds etc, which led to low utilisation of funds. The report also pointed out that; “the Committee found that despite having several monitoring mechanisms, the impact of MsDP is hardly visible in the Minority Concentration Areas”.
Weak processes and systems
There are six minority communities recognised and notified under Section 2(c) of the National Commission for Minorities Act, 1992 – Muslims, Sikhs, Christians, Buddhists, Zoroastrians and Jains. While the scheme initially targeted Minority Concentrated Districts (MCDs) with at least a 50% minority population, it was soon understood that the districts’ size was too big for the benefits to reach the grassroots. Thus, in 2012-14, the focus was shifted to Minority Concentration Blocks (MCB), Minority Concentration Towns (MCT) and Clusters of Minority Concentration Villages. Thus now, the grassroots level communities are directly targeted. This sharpened focus of the scheme reduced the stringent criteria, which seems beneficial for the communities that did not have the expected results at the grassroots level.Since its inception, the scheme been plagued by inefficient processes and systems, leading to substantial implementational hurdles. This scheme is monitored and regulated by various committees formed at various administrative levels such as the State Level Committee, District Level Committee, Block Level Committees, etc. However, it has been observed that the members in the Committees formed do not receive requisite training. This causes problems as they remain unclear on how to carry out their functions exactly. The unclarity further makes it difficult for these Committees to determine where/which infrastructure is to be developed. A second main factor working against the efficacy of PMJVK is the lack of awareness about the scheme at the ground level. In such situations of state failure, civil society organisations and non-governmental organisations are left to fulfil the state’s obligations. They have to step forward now and exert pressure on the authorities to declare clusters and identify projects.
This dilution in criteria has also, however, raised a concern too. The Sachar committee report, which paved the way for many minority-targeted schemes, including MsDP, was instrumental in demonstrating that the Muslim community lagged behind most communities on socio-economic indices. While reducing the population percentage parameter has ensured that the geographical coverage is more for the scheme, one of the primary beneficiaries (Muslims) is once again left with lesser resources.
—
The authors are associated with the Jharkhand Unit of the Centre for Social Justiceand are actively involved in providing legal representation to marginalised communities in Gumla. They may be contacted at rehnuma.jharkhand@gmail.com. Views are personal. This article was initially published in Newsclick

Comments